
Outline Lock-Based Protocols Timestamp-Based Protocols Validation-Based Protocols Multiple Granularity Multiversion Schemes Insert and Delete Operations Concurrency in Index Structures Database System Concepts-6th Edition 15.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 15.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Outline Lock-Based Protocols Timestamp-Based Protocols Validation-Based Protocols Multiple Granularity Multiversion Schemes Insert and Delete Operations Concurrency in Index Structures

Lock-Based Protocols A lock is a mechanism to control concurrent access to a data item Data items can be locked in two modes 1.exclusive ()mode.Data item can be both read as well as written.X-lock is requested using lock-X instruction. 2.shared(S)mode.Data item can only be read.S-lock is requested using lock-S instruction. Lock requests are made to the concurrency-control manager by the programmer.Transaction can proceed only after request is granted. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 15.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 15.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Lock-Based Protocols A lock is a mechanism to control concurrent access to a data item Data items can be locked in two modes : 1. exclusive (X) mode. Data item can be both read as well as written. X-lock is requested using lock-X instruction. 2. shared (S) mode. Data item can only be read. S-lock is requested using lock-S instruction. Lock requests are made to the concurrency-control manager by the programmer. Transaction can proceed only after request is granted
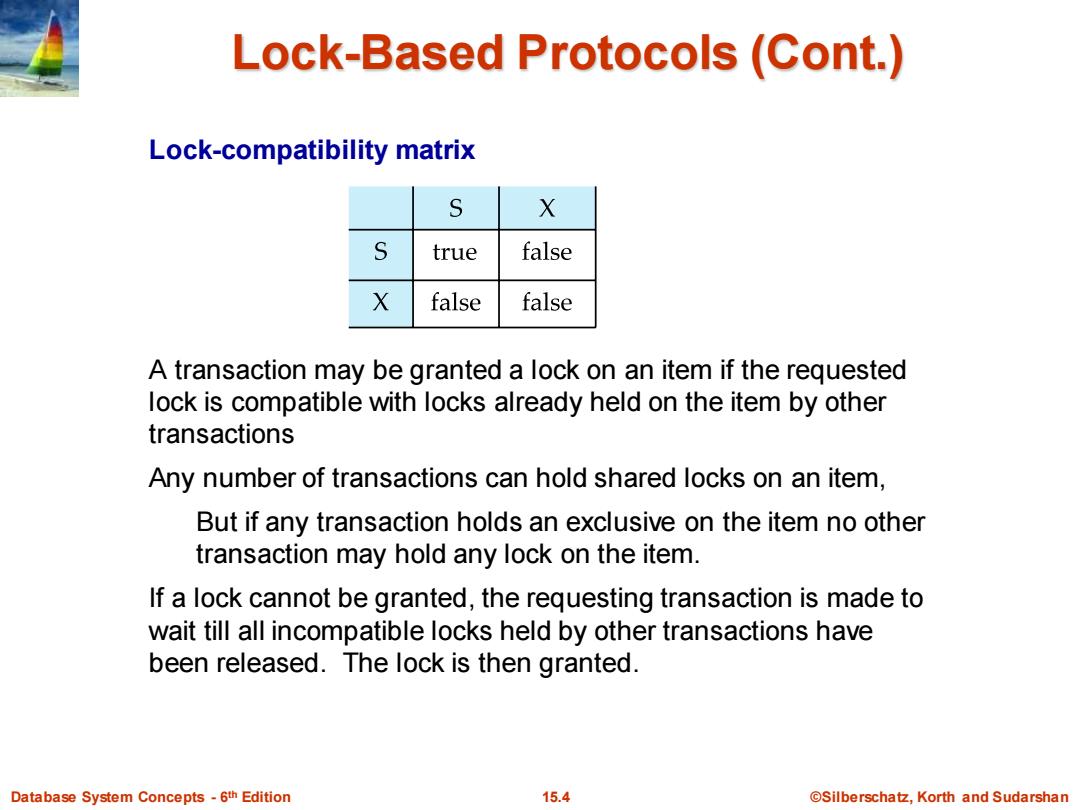
Lock-Based Protocols (Cont.) Lock-compatibility matrix S X S true false X false false A transaction may be granted a lock on an item if the requested lock is compatible with locks already held on the item by other transactions Any number of transactions can hold shared locks on an item, But if any transaction holds an exclusive on the item no other transaction may hold any lock on the item. If a lock cannot be granted,the requesting transaction is made to wait till all incompatible locks held by other transactions have been released.The lock is then granted. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 15.4 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 15.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Lock-Based Protocols (Cont.) Lock-compatibility matrix A transaction may be granted a lock on an item if the requested lock is compatible with locks already held on the item by other transactions Any number of transactions can hold shared locks on an item, But if any transaction holds an exclusive on the item no other transaction may hold any lock on the item. If a lock cannot be granted, the requesting transaction is made to wait till all incompatible locks held by other transactions have been released. The lock is then granted

Lock-Based Protocols (Cont.) Example of a transaction performing locking: T2:lock-S(A); read (A); unlock(A); lock-S(B); read (B); unlock(B); display(A+B) Locking as above is not sufficient to guarantee serializability -if A and B get updated in-between the read of A and B, the displayed sum would be wrong. A locking protocol is a set of rules followed by all transactions while requesting and releasing locks.Locking protocols restrict the set of possible schedules. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 15.5 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 15.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Lock-Based Protocols (Cont.) Example of a transaction performing locking: T2 : lock-S(A); read (A); unlock(A); lock-S(B); read (B); unlock(B); display(A+B) Locking as above is not sufficient to guarantee serializability — if A and B get updated in-between the read of A and B, the displayed sum would be wrong. A locking protocol is a set of rules followed by all transactions while requesting and releasing locks. Locking protocols restrict the set of possible schedules
The Two-Phase Locking Protocol This protocol ensures conflict-serializable schedules. Phase 1:Growing Phase Transaction may obtain locks Transaction may not release locks Phase 2:Shrinking Phase Transaction may release locks Transaction may not obtain locks The protocol assures serializability.It can be proved that the transactions can be serialized in the order of their lock points (i.e.,the point where a transaction acquired its final lock). Database System Concepts-6th Edition 15.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 15.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition The Two-Phase Locking Protocol This protocol ensures conflict-serializable schedules. Phase 1: Growing Phase Transaction may obtain locks Transaction may not release locks Phase 2: Shrinking Phase Transaction may release locks Transaction may not obtain locks The protocol assures serializability. It can be proved that the transactions can be serialized in the order of their lock points (i.e., the point where a transaction acquired its final lock)