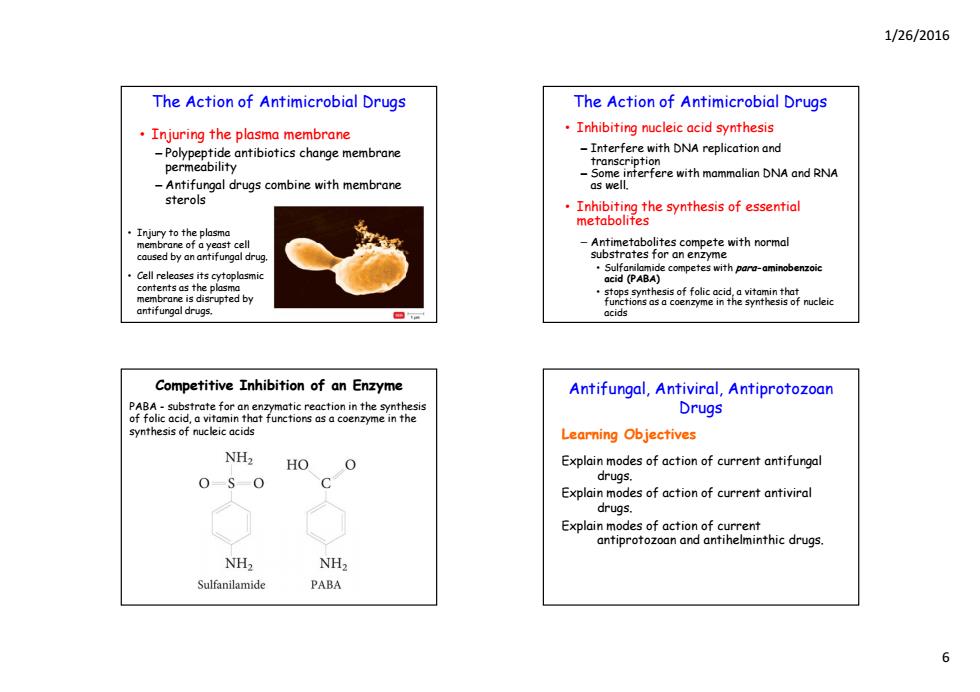
1/26/2016 The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs Injuring the plasma membrane Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis -Polypeptide antibiotics change membrane -Interfere with DNA replication and permeability transcription Some interfere with mammalian DNA and RNA -Antifungal drugs combine with membrane as well. sterols .Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites ·Injury to the plasma membrane of a yeast cell caused by an antifungal drug. trates for an enzyme Cell releases its cytoplasmic competeprminbenie contents as the plasma membrane is disrupted by ions as a coenzyme in antifungal drugs. Competitive Inhibition of an Enzyme Antifungal,Antiviral,Antiprotozoan PABA-substrate for an enzymatic reaction in the synthesis of folic acid,a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the Drugs synthesis of nucleic acids Learning Objectives NH2 HO O Explain modes of action of current antifungal 0-S0 C drugs. Explain modes of action of current antiviral drugs. Explain modes of action of current antiprotozoan and antihelminthic drugs. NH2 NH2 Sulfanilamide PABA 6
1/26/2016 6 The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs • Injuring the plasma membrane – Polypeptide antibiotics change membrane p m bilit permeability – Antifungal drugs combine with membrane sterols • Injury to the plasma membrane of a yeast cell caused by an antifungal drug. • Cell releases its cytoplasmic contents as the plasma membrane is disrupted by antifungal drugs. The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs • Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis – Interfere with DNA replication and transcr transcr pt on i i – Some interfere with mammalian DNA and RNA as well. • Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites – Antimetabolites compete with normal substrates for an enzyme • Sulfanilamide competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) • stops synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the synthesis of nucleic acids Competitive Inhibition of an Enzyme PABA - substrate for an enzymatic reaction in the synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in the synthesis of nucleic acids Antifungal, Antiviral, Antiprotozoan Drugs Learning Objectives Explain modes of action of current antifungal drugs. Explain modes of action of current antiviral drugs. Explain modes of action of current antiprotozoan and antihelminthic drugs
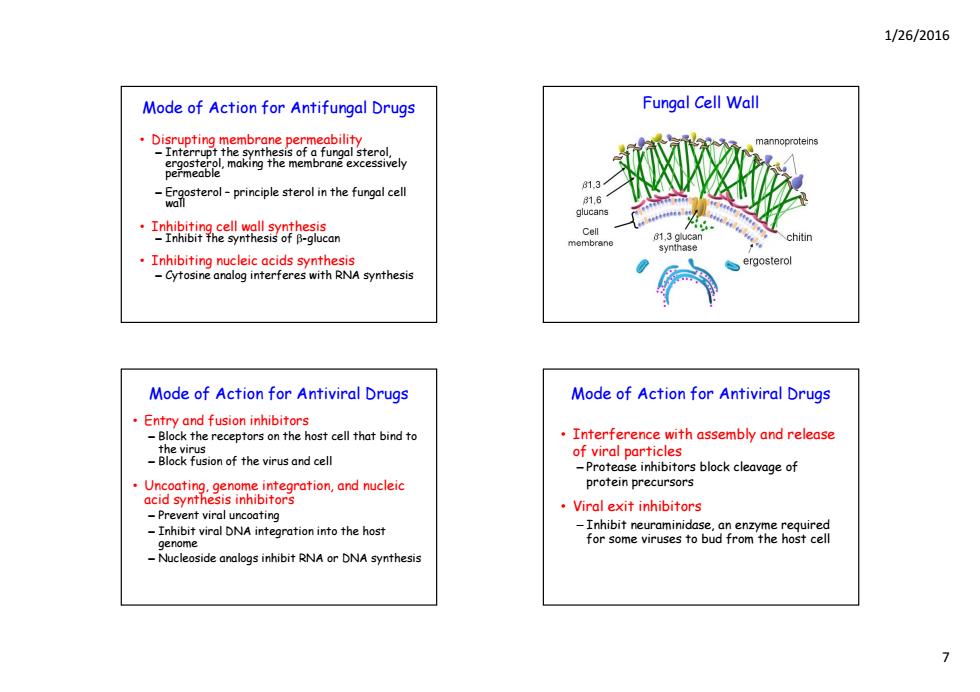
1/26/2016 Mode of Action for Antifungal Drugs Fungal Cell Wall oal sterol. mannoproteins 81.3 tero-principle sterol in the fungal cell 1日 Inhibiting cell wall synthesis -Inhibit the synthesis of B-glucan Cell chitin Inhibiting nucleic acids synthesis ergosterol -Cytosine analog interferes with RNA synthesis Mode of Action for Antiviral Drugs Mode of Action for Antiviral Drugs Entry and fusion inhibitors -Block the receptors on the host cell that bind to Interference with assembly and release the virus -Block fusion of the virus and cell of viral particles -Protease inhibitors block cleavage of Uncoating.genome integration,and nucleic protein precursors acid synthesis inhibitors Viral exit inhibitors -Prevent viral uncoating Inhibit viral DNA integration into the host -Inhibit neuraminidase,an enzyme required genome for some viruses to bud from the host cell -Nucleoside analogs inhibit RNA or DNA synthesis >
1/26/2016 7 Mode of Action for Antifungal Drugs • Disrupting membrane permeability – Interrupt the synthesis of a fungal sterol, ergosterol making the membrane excessively ergosterol, making the membrane excessively permeable – Ergosterol – principle sterol in the fungal cell wall • Inhibiting cell wall synthesis – Inhibit the synthesis of -glucan • Inhibiting nucleic acids synthesis – Cytosine analog interferes with RNA synthesis Fungal Cell Wall • Entry and fusion inhibitors – Block the receptors on the host cell that bind to the virus Mode of Action for Antiviral Drugs – Block fusion of the virus and cell • Uncoating, genome integration, and nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors – Prevent viral uncoating – I hibi i l DNA i i i h h Inhibit viral DNA integration into the host genome – Nucleoside analogs inhibit RNA or DNA synthesis • Interference with assembly and release f i l ti l Mode of Action for Antiviral Drugs of viral particles – Protease inhibitors block cleavage of protein precursors • Viral exit inhibitors – Inhibit neuraminidase an enzyme required Inhibit neuraminidase, an enzyme required for some viruses to bud from the host cell