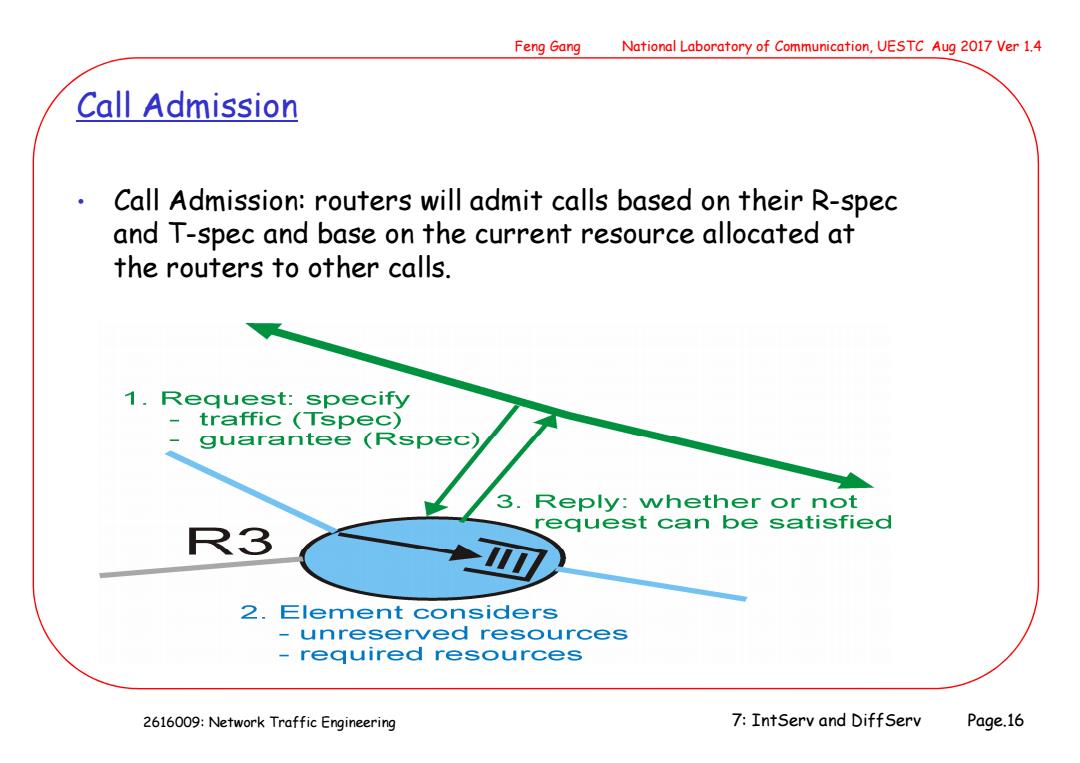
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Call Admission 。 Call Admission:routers will admit calls based on their R-spec and T-spec and base on the current resource allocated at the routers to other calls. 1.Request:specify traffic (Tspec) guarantee (Rspec) 3.Reply:whether or not request can be satisfied R3 ◆0 2.Element considers -unreserved resources required resources 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 7:IntServ and DiffServ Page.16
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 7: IntServ and DiffServ Page.16 Call Admission • Call Admission: routers will admit calls based on their R-spec and T-spec and base on the current resource allocated at the routers to other calls
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Flow Specification Flow Spec Traffic Spec QoS Spec TSpec RSpec TSpec:Peak rate (p),bucket rate(r),bucket size (b),max datagram size(M),min policed unit (m) All datagrams less than m are counted as m bytes Peak rate may be unknown or unspecified RSpec:Rate(R)and delay slack (S) S Extra acceptable delay over that obtainable with R Zero slack Reserve exactly R. 。 RSpec specified only for guaranteed rate service. Not for controlled load service. 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 7:IntServ and DiffServ Page.17
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 7: IntServ and DiffServ Page.17 Flow Specification • Flow Spec = Traffic Spec + QoS Spec = TSpec + RSpec • TSpec: Peak rate (p), bucket rate (r), bucket size (b), max datagram size (M), min policed unit (m) - All datagrams less than m are counted as m bytes - Peak rate may be unknown or unspecified • RSpec: Rate (R) and delay slack (S) S = Extra acceptable delay over that obtainable with R Zero slack Reserve exactly R. • RSpec specified only for guaranteed rate service. Not for controlled load service

Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 Reservation and Admission Protocols The resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP)was developed to communicate resource needs between hosts and network devices (RFC2205-2215) Common Open Policy Service (COPS)was developed to offload admission control to a central policy server (RFC 2748-2753) 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 7:IntServ and DiffServ Page.18
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 7: IntServ and DiffServ Page.18 Reservation and Admission Protocols - The resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP) was developed to communicate resource needs between hosts and network devices (RFC 2205-2215) - Common Open Policy Service (COPS) was developed to offload admission control to a central policy server (RFC 2748-2753)
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 RSVP-enabled Applications RSVP is typically used by applications carrying voice or video over IP networks (initiated by a host) RSVP with extensions is also used by MPLS Traffic . Engineering to establish MPLS/TE tunnels (initiated by a router) 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 7:IntServ and DiffServ Page.19
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 7: IntServ and DiffServ Page.19 RSVP-enabled Applications - RSVP is typically used by applications carrying voice or video over IP networks (initiated by a host) - RSVP with extensions is also used by MPLS Traffic Engineering to establish MPLS/TE tunnels (initiated by a router)
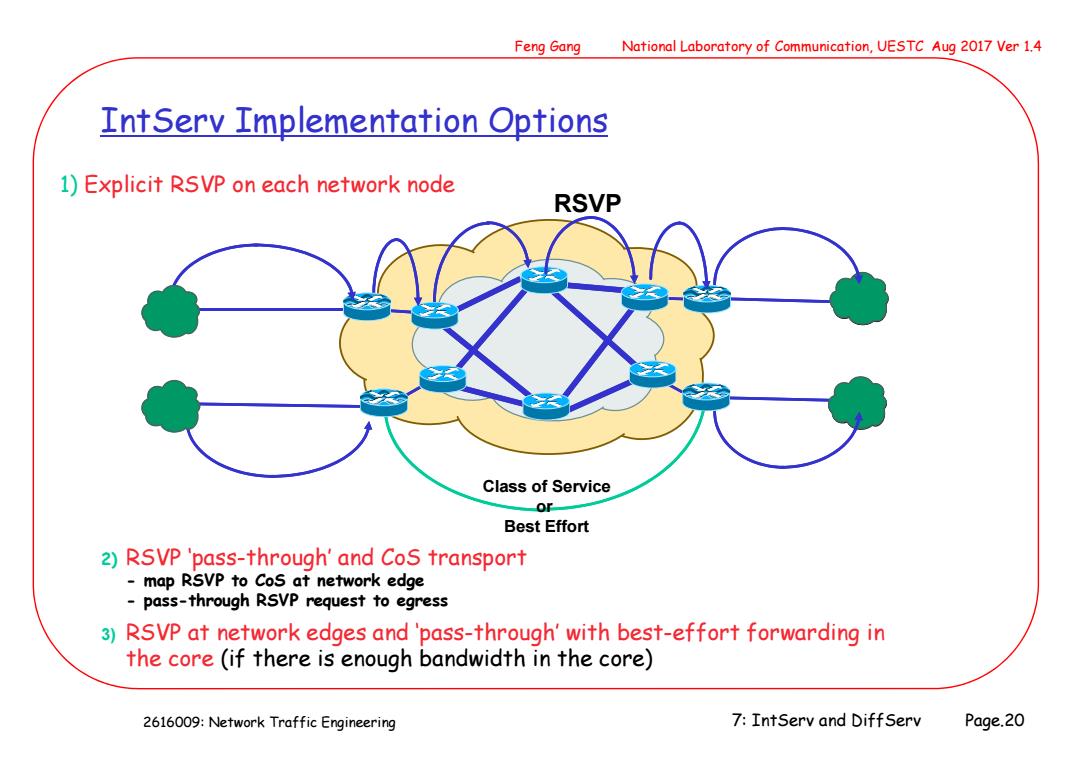
Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication,UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 IntServ Implementation Options 1)Explicit RSVP on each network node RSVP Class of Service or Best Effort 2)RSVP 'pass-through'and CoS transport map RSVP to CoS at network edge pass-through RSVP request to egress 3)RSVP at network edges and 'pass-through'with best-effort forwarding in the core (if there is enough bandwidth in the core) 2616009:Network Traffic Engineering 7:IntServ and DiffServ Page.20
2616009: Network Traffic Engineering Feng Gang National Laboratory of Communication, UESTC Aug 2017 Ver 1.4 7: IntServ and DiffServ Page.20 IntServ Implementation Options 1) Explicit RSVP on each network node 2) RSVP ‘pass-through’ and CoS transport - map RSVP to CoS at network edge - pass-through RSVP request to egress RSVP Class of Service or Best Effort 3) RSVP at network edges and ‘pass-through’ with best-effort forwarding in the core (if there is enough bandwidth in the core)