
提纲 File Concept Access Methods(访问方式) Directory Structure(目录结构) File System Mounting(文件系统挂载, File sharing(文件共享) Protection 小结和作业 4口”4814在,4色,主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 提纲 File Concept Access Methods (访问方式) Directory Structure (目录结构) File System Mounting (文件系统挂载) File sharing (文件共享) Protection 小结和作业
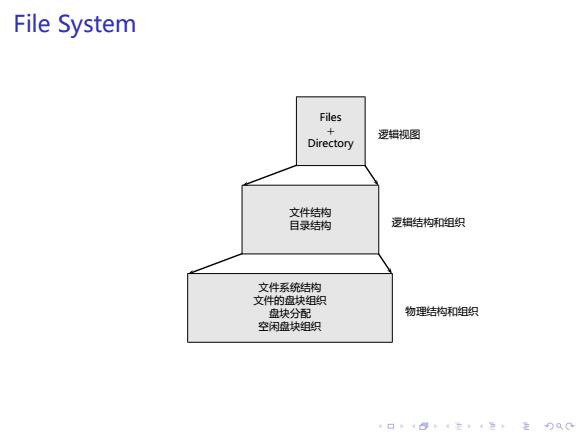
File System Files 逻辑视图 Directory 文件结构 目录结构 逻辑结构和组织 文件系统结构 文件的盘块组织 盘块分配 物理结构和组织 空闲盘块组织 口·484在,4生,主Q0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . File System 逻辑视图 逻辑结构和组织 物理结构和组织 文件系统结构 文件的盘块组织 盘块分配 空闲盘块组织 文件结构 目录结构 Files + Directory

Chapter Ojbectives To explain the function of file systems To describe the interfaces to file systems To discuss file-system design tradeoffs,including access methods,file sharing,file locking,and directory structures To explore file-system protection 4口”4814在,4色,主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Chapter Ojbectives ▶ To explain the function of file systems ▶ To describe the interfaces to file systems ▶ To discuss file-system design tradeoffs, including access methods, file sharing, file locking, and directory structures ▶ To explore file-system protection

Outline File Concept 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline File Concept
File Concept OS provides a uniform logical view of infomation storage despite the various storage media (nonvolatile). A file is a logical storage unit. A file is a named collection of related information that is recorded on secondary storage. Types: Data:numeric;character;binary Program In general,a file is a sequence of bits,bytes,lines,or records. The meaning is defined by the file's creator and user. A file has a certain defined structure,which depends on its type. Example:text files,source files,object files,executable files Contiguous logical address space 145+4在4生,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . File Concept ▶ OS provides a uniform logical view of infomation storage despite the various storage media (nonvolatile). ▶ A file is a logical storage unit. ▶ A file is a named collection of related information that is recorded on secondary storage. ▶ Types: ▶ Data: numeric; character; binary ▶ Program ▶ In general, a file is a sequence of bits, bytes, lines, or records. ▶ The meaning is defined by the file’s creator and user. ▶ A file has a certain defined structure, which depends on its type. ▶ Example: text files, source files, object files, executable files ▶ Contiguous logical address space