
9/18/2016 Learning Objectives Food 1.Use basic biochemical characteristics to identify Microbiology Campylobacter species 2.Understand what conditions in foods favor Chapter 9 AN INTRODUCTION Campylobacter species growth 3.Recognize,from symptoms and time of onset,a case of foodborne illness caused by a Campylobacter Campylobacter species species 4.Choose appropriate interventions to prevent the growth of Campylobacter species 5.Identify environmental sources of the organism 6.Understand the roles of Campylobacter species toxins and virulence factors in causing foodborne illness Outbreak ·Outbreak Campylobacteraceae Family 2002,86 preschoolers and adults visited a farm in Kansas Genera Campylobacter and Arcobacter Walked through the farm,petted animals and sampled raw milk Family grows as new species and 65 of the 86 who sampled the milk became ill subspecies are discovered -Campylobacteriosis diarrhea and dehydration .Campylobacter jejuni subsp. ·Outbreak2 Jjejuni is the best studied of Also in Kansas,67 of 101 individuals who fresh cheese a fair many species and subspecies Curved,S-shaped,or spiral rod The cheese was made from unpasteurized milk Campylobacterin a farm ervironment is not unusual Pasteurization effectively kills Campylobacter jejuni 1
9/18/2016 1 Chapter 9 Campylobacter spec es i Learning Objectives 1. Use basic biochemical characteristics to identify Campylobacter species 2. Understand what conditions in f f oodsavor Campylobacter species growth 3. Recognize, from symptoms and time of onset, a case of foodborne illness caused by a Campylobacter species 4. Choose appropriate interventions to prevent the growth of Campylobacter species 5. Identify environmental sources of the organism 6. Understand the roles of Campylobacter species toxins and virulence factors in causing foodborne illness Outbreak • Outbreak 1 - 2002, 86 preschoolers and adults visited a farm in Kansas - W lk d th h th f tt d i ls d s l d Walked through the farm, petted animals and sampled raw milk - 65 of the 86 who sampled the milk became ill - Campylobacteriosis – diarrhea and dehydration • Outbreak 2 - Also in Kansas, 67 of 101 individuals who consumed fresh cheese at a fair and picnic developed campylobacteriosis - The cheese was made from unpasteurized milk • Campylobacter in a farm environment is not unusual • Pasteurization effectively kills Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacteraceae Family • Genera Campylobacter and Arcobacter • F il i d Family grows as new species and subspecies are discovered • Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni is the best studied of many species and subspecies • Curved, S-shaped, or spiral rods

9/18/2016 Campylobacteraceae Family Campylobacteraceae Family Gram-negative,non-spore-forming rods that form coccoid bodies in old cultures Microaerophilic-requires oxygen for or cultures that are exposed to air too growth but at lower concentration than is long present in the atmosphere Motile via a single polar flagellum at one 5%oxygen and 10%carbon dioxide or both ends Respiratory type metabolism Some strains grow aerobically and anaerobically Genome is one-third the size(1.7 megabases)of Escherichia coli(4.6 Mbs) Environmental Susceptibility Environmental Susceptibility .C.jejunisurvives only a short period Susceptible to gamma irradiation but outside of its host killing depends on the food product does not grow below 30C less effective for frozen foods -microaerophilic ·Killed at pH2.3 sensitive to drying,high oxygen,and Grow in bile at 37C survive better in low pH feces,milk,water,and urine held at 4C Adequate cooking temperatures will kill than at 25C C.jejuni Freezing reduces the number in poultry and raw meat
9/18/2016 2 Campylobacteraceae Family • Gram-negative, non-spore-forming rods that form coccoid bodies in old cultures or l h d cultures that are exposed to air too long • Motile via a single polar flagellum at one or both ends • Microaerophilic - requires oxygen for growth but at lower concentration than is Campylobacteraceae Family present in the atmosphere • 5% oxygen and 10% carbon dioxide • Respiratory type metabolism • Some strains grow aerobically and anaerobically • Genome is one-third the size (1.7 megabases) of Escherichia coli (4.6 Mbs) Environmental Susceptibility • C. jejuni survives only a short period out id f it h t tside of its host - does not grow below 30oC - microaerophilic - sensitive to drying, high oxygen, and low pH • Adequate cooking temperatures will kill C. jejuni Environmental Susceptibility • Susceptible to gamma irradiation but killing depends on the food product - less effective for frozen foods • Killed at pH 2.3 • Grow in bile at 37oC survive better in feces milk water and urine held at 4 feces, milk, water, and urine held at 4oC than at 25oC • Freezing reduces the number in poultry and raw meat
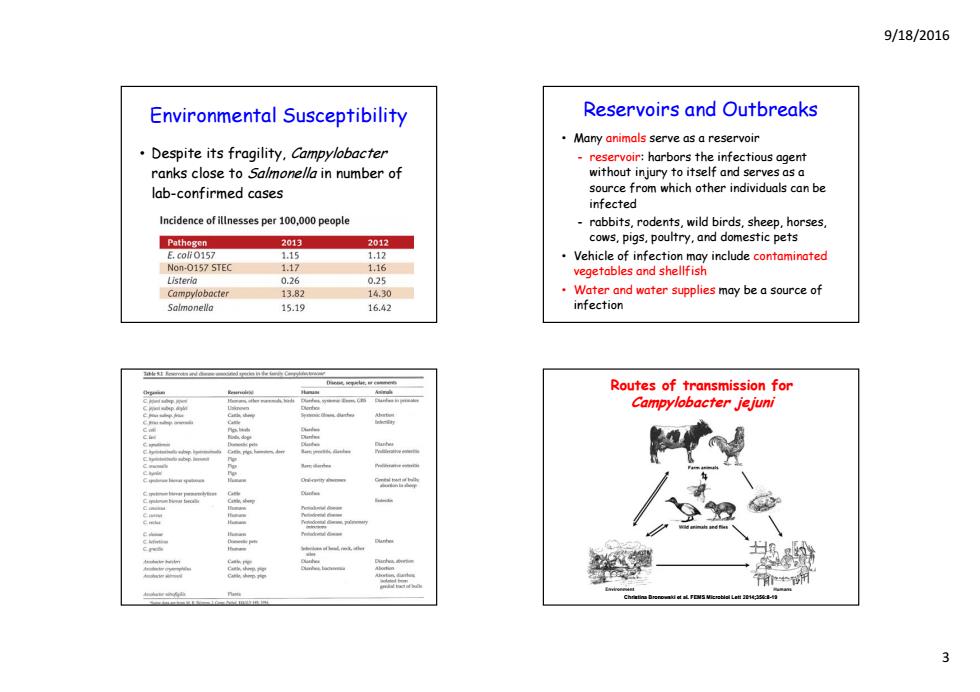
9/18/2016 Environmental Susceptibility Reservoirs and Outbreaks Many animals serve as a reservoir Despite its fragility,Campylobacter reservoir:harbors the infectious agent ranks close to Salmone/la in number of without injury to itself and serves as a lab-confirmed cases source from which other individuals can be infected Incidence of illnesses per 100,000 people rabbits,rodents,wild birds,sheep,horses 2013 2012 cows,pigs,poultry,and domestic pets 1.12 Vehicle of infection may include contaminated Non-0157 STEC 1.17 1,16 vegetables and shellfish Listeria 0.26 0.25 Campylobocter 13.82 14.30 Water and water supplies may be a source of 15.19 16.42 infection Routes of transmission for Campylobacter jejuni 三
9/18/2016 3 Environmental Susceptibility • Despite its fragility, Campylobacter ranks close to Salmonella in number of lab-confirmed cases Reservoirs and Outbreaks • Many animals serve as a reservoir - reservoir: harbors the infectious agent without injury to itself and serves as a source from which other individuals can be infected - rabbits, rodents, wild birds, sheep, horses, cows, pg p y p igs, poultry, and domestic pets • Vehicle of infection may include contaminated vegetables and shellfish • Water and water supplies may be a source of infection Routes of transmission for Campylobacter jejuni Christina Bronowski et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2014;356:8-19

9/18/2016 Campylobacteriosis is a global health problem C.jejuni can remain dormant in water in the VBNC state Viable but nonculturable(VBNC)bacteria bacteria that are in a state of very low metabolic activity and do not divide,but are alive and have the ability to become culturable once resuscitated ·Not easily recovered on growth media ·May be source of infection though their :28:657.720 role is unknown Vehicle of outbreaks changed over the Product %Positive samples tg decades 325 -1978-1987-water,unpasteurized 3 milk Cow's milk 123 -1988-1996-other foods Goat's milk 0 Ewe's milk predominated 0-236 At least one outbreak each year 1-235 Lamb 0-155 Most involved children who had taken field trips to dairy farms Mussels 5
9/18/2016 4 • C. jejuni can remain dormant in water in the VBNC state • Viable but nonculturable (VBNC) bacteria - bacteria that are in a state of very low metabolic activity and do not divide, but are alive and have the ability to become culturable once resuscitated • Not easily recovered on h di growth media • May be source of infection though their role is unknown Campylobacteriosis is a global health problem Nadeem O. Kaakoush et al. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015;28:687-720 • Vehicle of outbreaks changed over the decades - 1978-1987 – water, unpasteurized milk - 1988-1996 – other foods predominated • At least one outbreak each year • M t i l d hild h h d t k Most involved children who had taken field trips to dairy farms
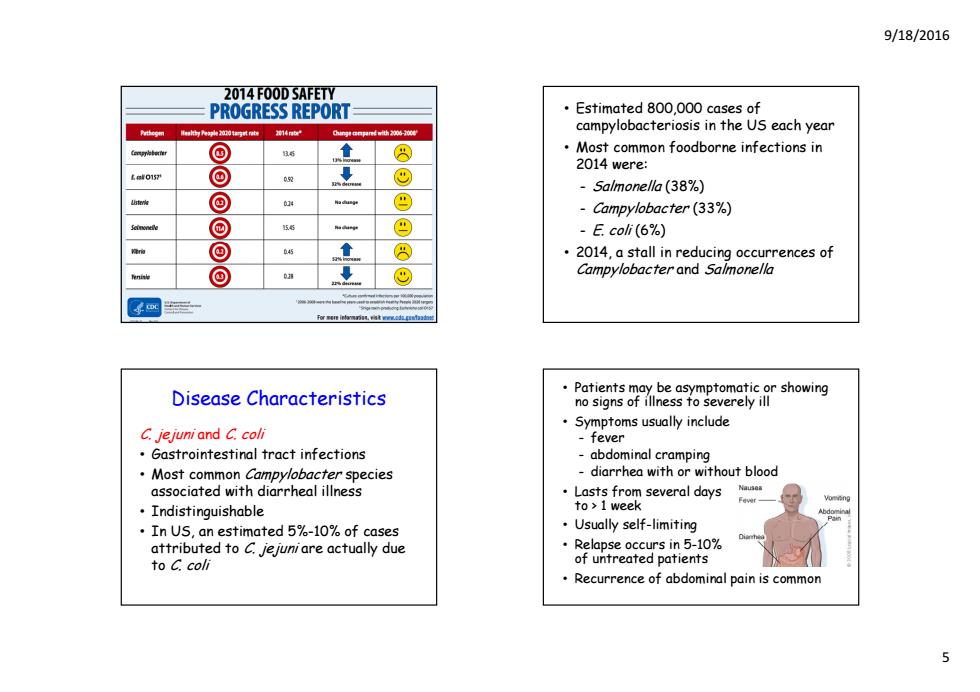
9/18/2016 2014 FOOD SAFETY PROGRESS REPORT Estimated 800,000 cases of 4a古学 campylobacteriosis in the US each year © 8 Most common foodborne infections in 2014 were: ▣ 05段 © Salmonella(38%) ▣ 64 ⑨ Campylobacter (33%) 回 E.coli(6%) ⑨ 045 8 2014,a stall in reducing occurrences of © Campylobacter and Salmonella Disease Characteristics Patients may be asymptomatic or showing no signs of illness to severely ill Symptoms usually include C jejuni and C.coli -fever Gastrointestinal tract infections -abdominal cramping Most common Campylobacter species -diarrhea with or without blood associated with diarrheal illness Lasts from several days ·Indistinguishable to>1 week In US,an estimated 5%-10%of cases Usually self-limiting attributed to C.jejuni are actually due Relapse occurs in 5-10% to C.coli of untreated patients Recurrence of abdominal pain is common
9/18/2016 5 • Estimated 800,000 cases of campylobacteriosis in the US each year • Most common foodborne infections in 2014 were: - Salmonella (38%) - Campylobacter (33%) - E. coli (6%) • 2014, a stall in reducing occurrences of Campylobacter and Salmonella Disease Characteristics C. jejuni and C. coli • Gastrointestinal tract infections • Most common Campylobacter species associated with diarrheal illness • Indistinguishable • I US i d 5% In US, an estimated 5%-10% f o cases attributed to C. jejuni are actually due to C. coli • Patients may be asymptomatic or showing no signs of illness to severely ill • Symptoms usually include - fever - abdominal cramping - diarrhea with or without blood • Lasts from several days to > 1 week • Usually self-limiting • Relapse occurs in 5-10% of untreated patients • Recurrence of abdominal pain is common