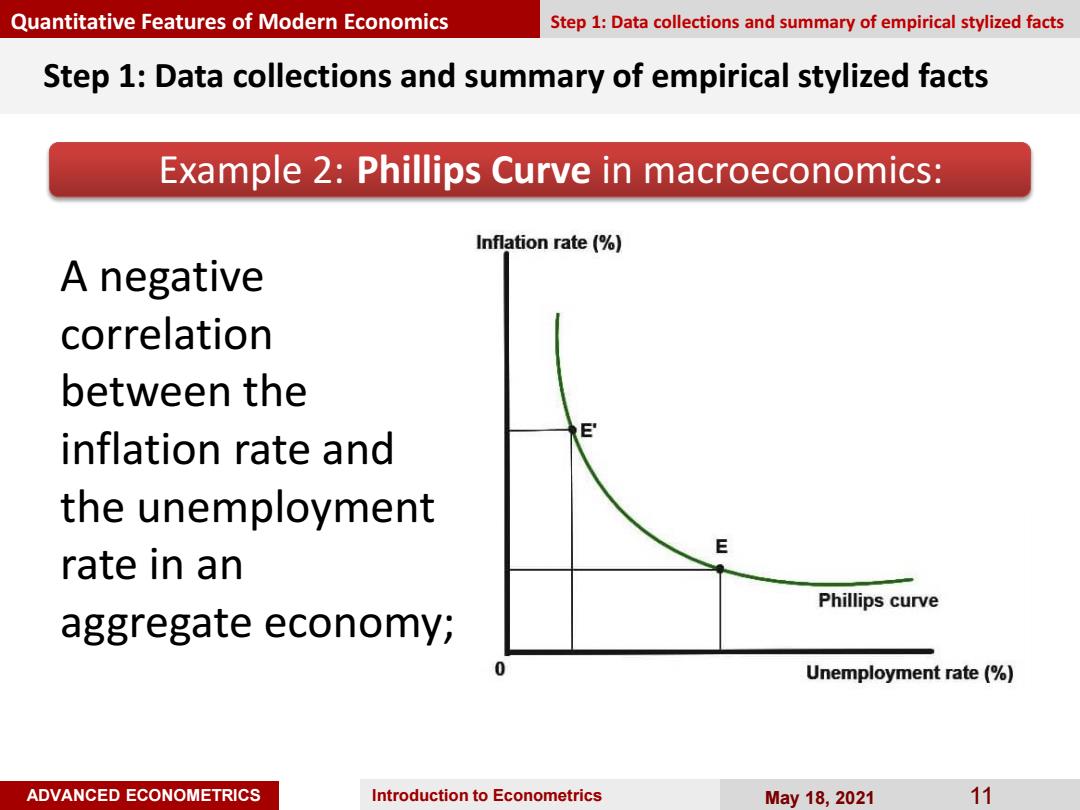
Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2:Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: Inflation rate (% A negative correlation between the E inflation rate and the unemployment E rate in an Phillips curve aggregate economy; 0 Unemployment rate (% ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 11
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 11 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2: Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts A negative correlation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate in an aggregate economy;

Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3:volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow,a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow,and both alternate over time. MlhMonlAwlhd 竹,T 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 time ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 12
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 12 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3: volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow, a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow, and both alternate over time. Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts

Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts a starting point the empirical serve as for economic stylized facts research ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 13
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 13 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts the empirical stylized facts a starting point for economic research serve as

Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections /models /inference With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 14
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 14 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models ● With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. ● This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 2: Development of economic theories/models Data collections Economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications
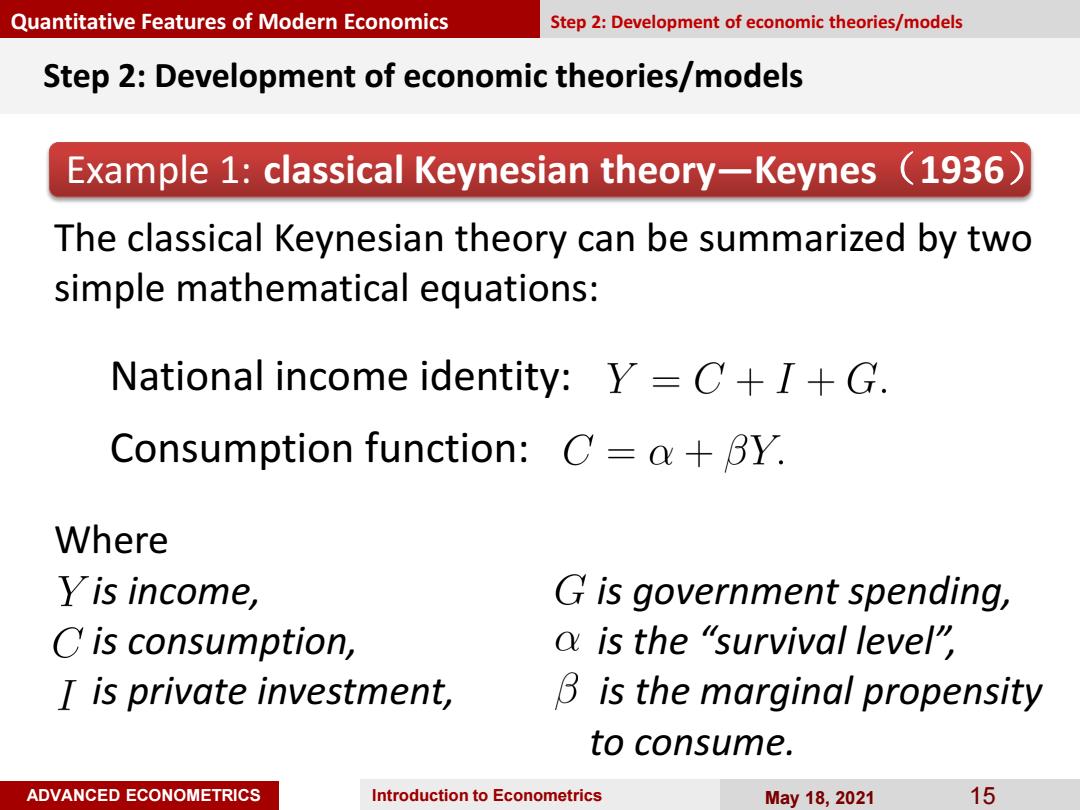
Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Example 1:classical Keynesian theory-Keynes (1936) The classical Keynesian theory can be summarized by two simple mathematical equations: National income identity:Y=C+I+G. Consumption function:C=a+BY. Where Yis income, G is government spending, C is consumption, a is the "survival level" I is private investment, B is the marginal propensity to consume. ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 15
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 15 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models Example 1: classical Keynesian theory—Keynes(1936) The classical Keynesian theory can be summarized by two simple mathematical equations: Where is income, is government spending, is consumption, is the “survival level”, is private investment, is the marginal propensity to consume. Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 2: Development of economic theories/models National income identity: Consumption function: