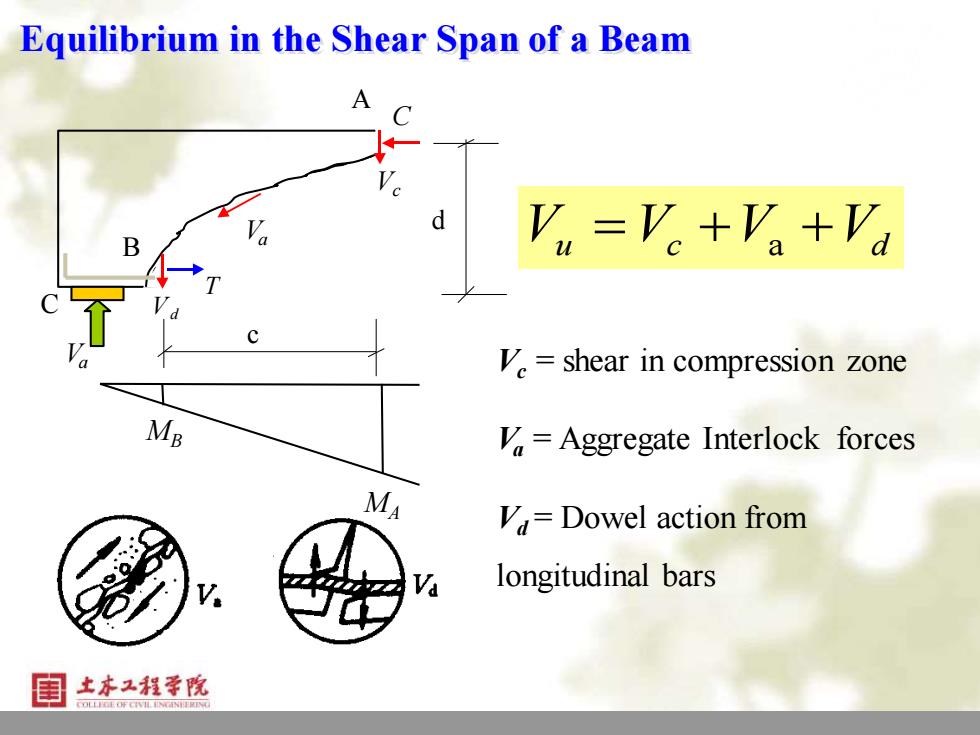
Equilibrium in the Shear Span of a Beam A Vx=Ve+Va+Va V.=shear in compression zone Me =Aggregate Interlock forces MA V=Dowel action from Va longitudinal bars 土本工程学脱 COLC特CN有CN情展网
11 Equilibrium in the Shear Span of a Beam Vc = shear in compression zone Va = Aggregate Interlock forces Vd = Dowel action from longitudinal bars V V V V u c d = + +a Vd T MB MA A B C Va Vc C c Va d

Principal Mechanism of Shear Resistance v-dM-d(d)ddd) dx dx d dx jd=constant,v= id qid dx Compression zone acki (1)Before dow (3)After cracking.with stirrup (2)After dowel cracking,without stirrup 目土本工程学院 Dowel displacement△
12 Principal Mechanism of Shear Resistance dM dT d Tjd d jd ( ) ( ) V jd T dx dx dx dx = = = + constant, dT jd V jd qjd dx = = = Beam action 20% by flexure at built-in end <25% by dowel action 50~70% by aggregate interlock For beams without web reinforcement: Vc only 25~40% of total shear force

Principal Mechanism of Shear Resistance V- Md(d)d d(jd dx dx dx d T=constant,v=7d(jd) Line of thrust ressive arch sline 土本又程学院 COLLIOEOF CIVILINGANEE RING
13 Principal Mechanism of Shear Resistance dM dT d Tjd d jd ( ) ( ) V jd T dx dx dx dx = = = + ( ) constant, d jd T V T dx = = Arch action arch brace Compressive stress line

B-and D-Regions B-region:beam action D-region:arch action 4 One member depth each way from concentrated loads,reactions,or abrupt changes in section or direction 目土本工程学院
14 B- and D-Regions B-region: beam action D-region: arch action One member depth each way from concentrated loads, reactions, or abrupt changes in section or direction
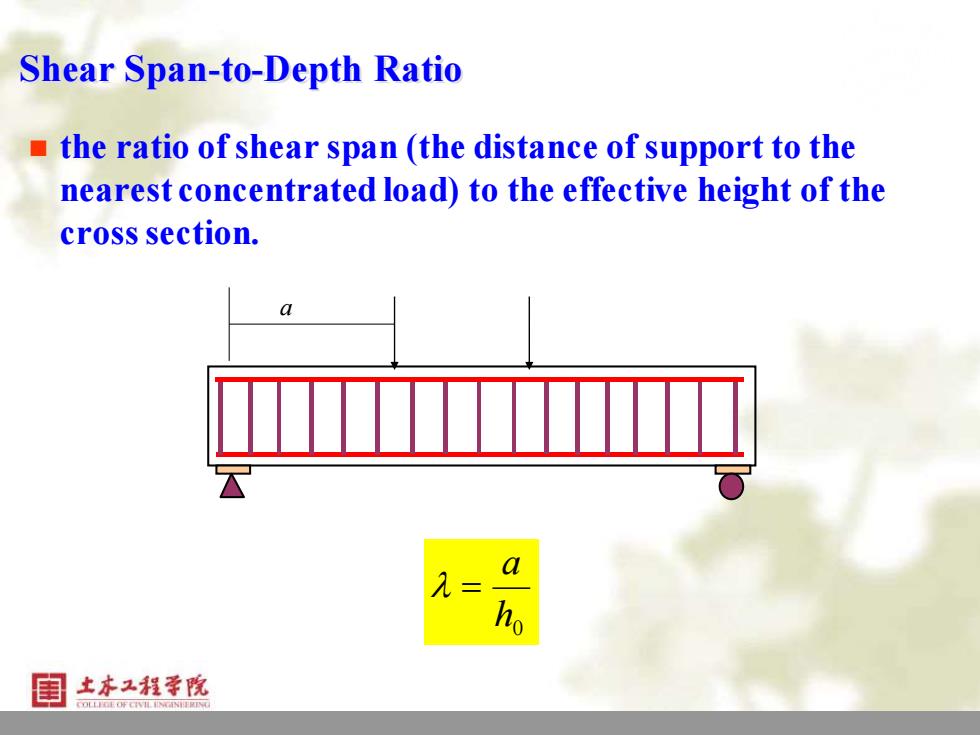
Shear Span-to-Depth Ratio the ratio of shear span(the distance of support to the nearest concentrated load)to the effective height of the cross section. a 土本又程学院
15 Shear Span-to-Depth Ratio ◼ the ratio of shear span (the distance of support to the nearest concentrated load) to the effective height of the cross section. h0 a = a