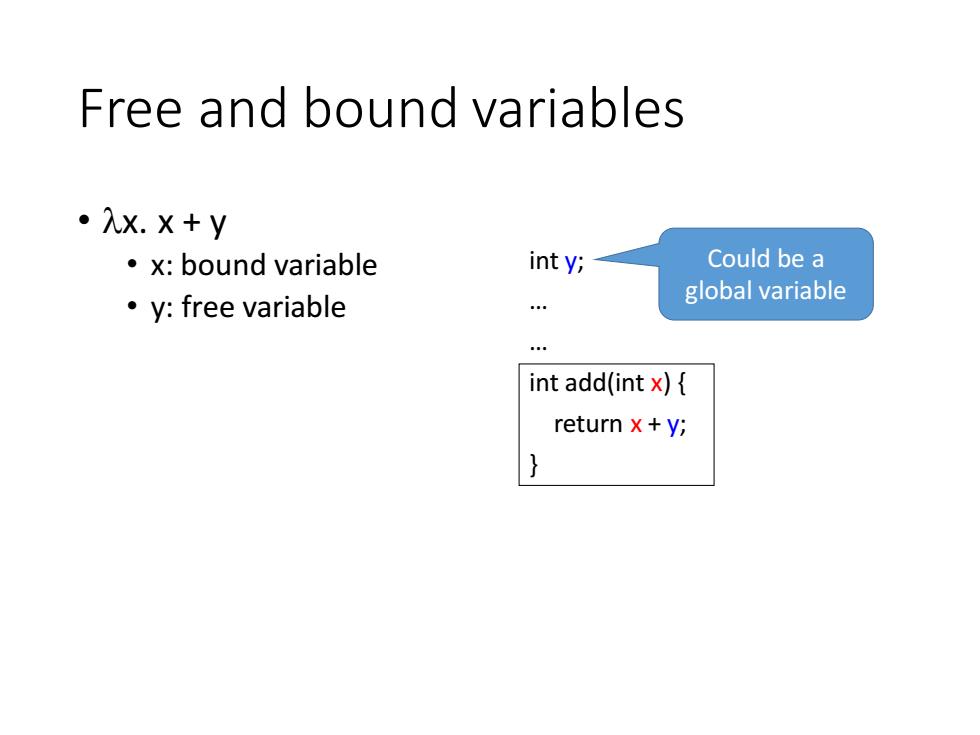
Free and bound variables 。入x.×+y ·x:bound variable int y; Could be a global variable 。y:free variable int add(int x){ return x+y;
Free and bound variables • x. x + y • x: bound variable • y: free variable int y; … … int add(int x) { return x + y; } Could be a global variable
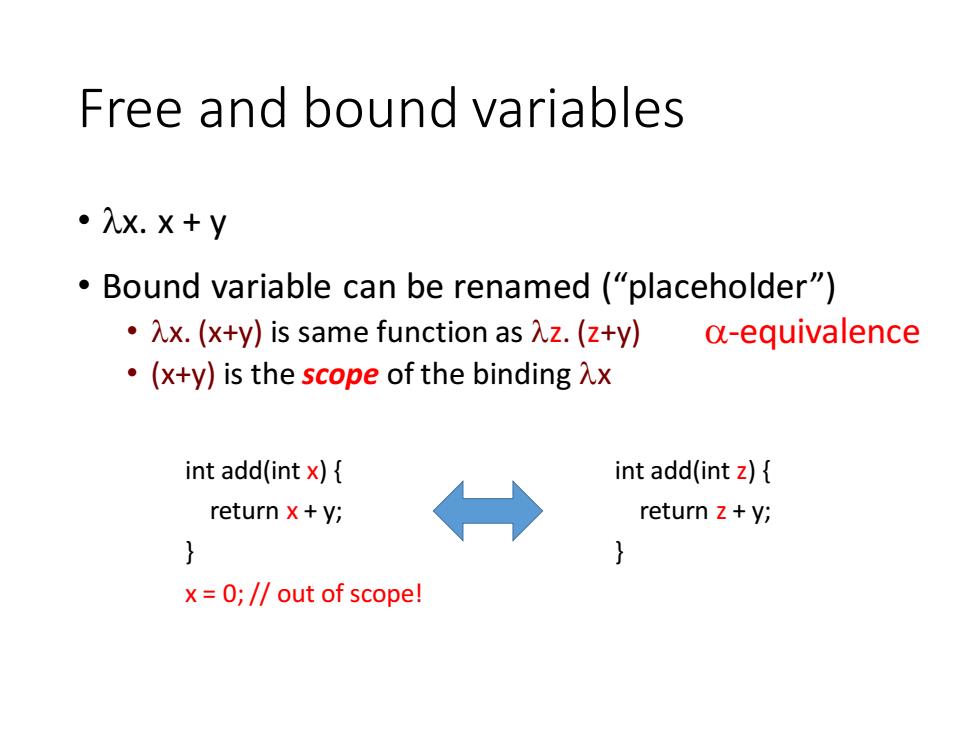
Free and bound variables 。入x.X+y Bound variable can be renamed ("placeholder") ·x.(x+y)is same function as入z.(z+y) a-equivalence ·(x+y)is the scope of the binding入x int add(int x){ int add(int z){ return x+y; → return z+y; } x=0;//out of scope!
Free and bound variables • x. x + y • Bound variable can be renamed (“placeholder”) • x. (x+y) is same function as z. (z+y) • (x+y) is the scope of the binding x int add(int x) { return x + y; } int add(int z) { return z + y; } x = 0; // out of scope! -equivalence
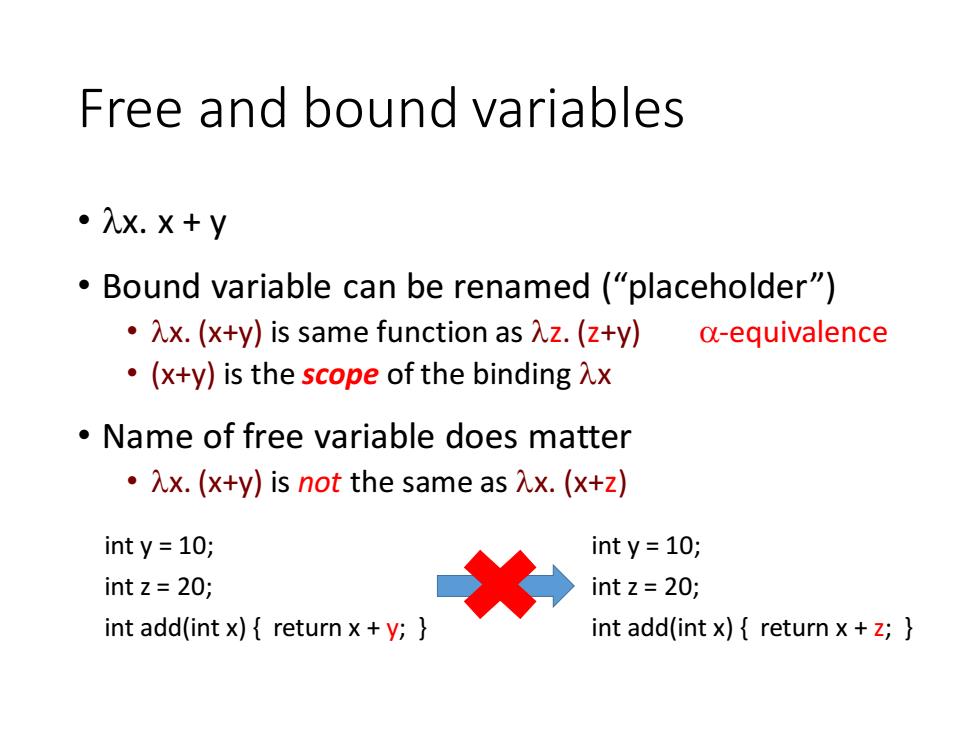
Free and bound variables ·入x.×+y Bound variable can be renamed ("placeholder") ·x.(x+y)is same function as入z.(z+y) a-equivalence .(x+y)is the scope of the binding Ax Name of free variable does matter 。x.(x+y)is not the same as入x.(x+z) int y=10; int y=10; int z=20; int z=20; int add(int x){return x+y;} int add(int x){return x+z;}
Free and bound variables • x. x + y • Bound variable can be renamed (“placeholder”) • x. (x+y) is same function as z. (z+y) -equivalence • (x+y) is the scope of the binding x • Name of free variable does matter • x. (x+y) is not the same as x. (x+z) int y = 10; int z = 20; int add(int x) { return x + y; } int y = 10; int z = 20; int add(int x) { return x + z; }
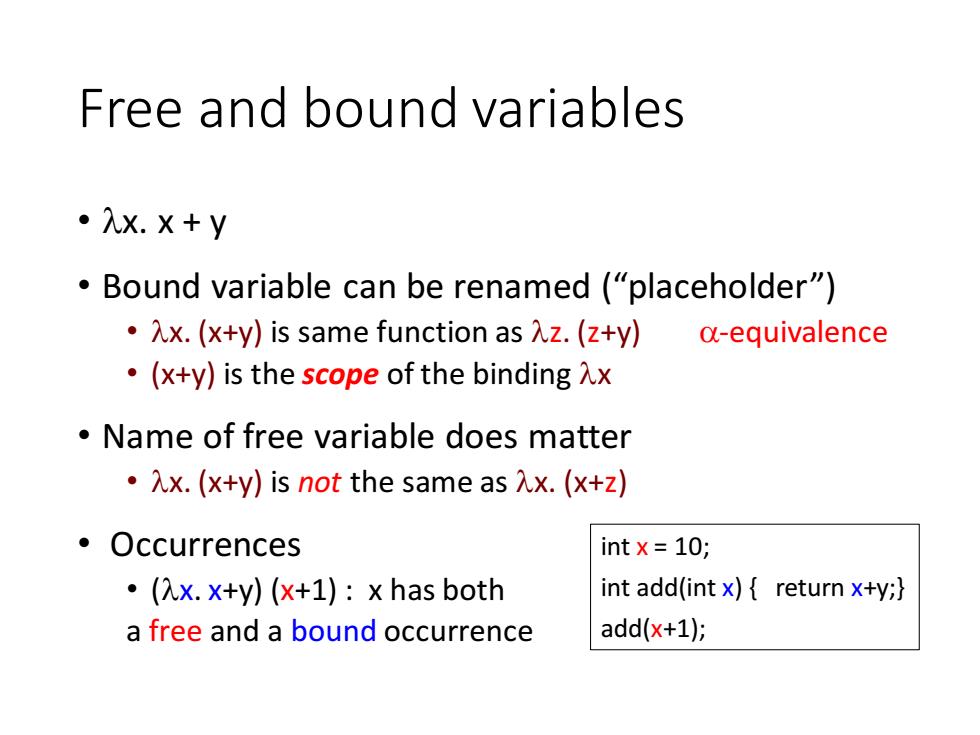
Free and bound variables 。入x.X+y Bound variable can be renamed ("placeholder") Xx.(x+y)is same function as Az.(z+y) a-equivalence ·(x+y)is the scope of the binding入x Name of free variable does matter ·x.(x+y)is not the same as入x.(x+z) ·Occurrences int x=10; (7x.x+y)(x+1):x has both int add(int x){return x+y; a free and a bound occurrence add(x+1);
Free and bound variables • x. x + y • Bound variable can be renamed (“placeholder”) • x. (x+y) is same function as z. (z+y) -equivalence • (x+y) is the scope of the binding x • Name of free variable does matter • x. (x+y) is not the same as x. (x+z) • Occurrences • (x. x+y) (x+1) : x has both a free and a bound occurrence int x = 10; int add(int x) { return x+y;} add(x+1);

Formal definitions about free and bound variables 。Recall M,N:=xI入x.MIMN fv(M):the set of free variables in M fv(x)≡{x f(2x.M)=f(M)\{x Defined by induction on terms fv(MN)≡fv(M)Ufv(N) 。Example fv((Ax.x)x)={x} fv((Ax.x+y)x)={x,y}
Formal definitions about free and bound variables • Recall M, N ::= x | x. M | M N • fv(M): the set of free variables in M fv(x) {x} fv(x.M) fv(M) \ {x} fv(M N) fv(M) fv(N) • Example fv((x. x) x) = {x} fv((x. x + y) x) = {x, y} Defined by induction on terms