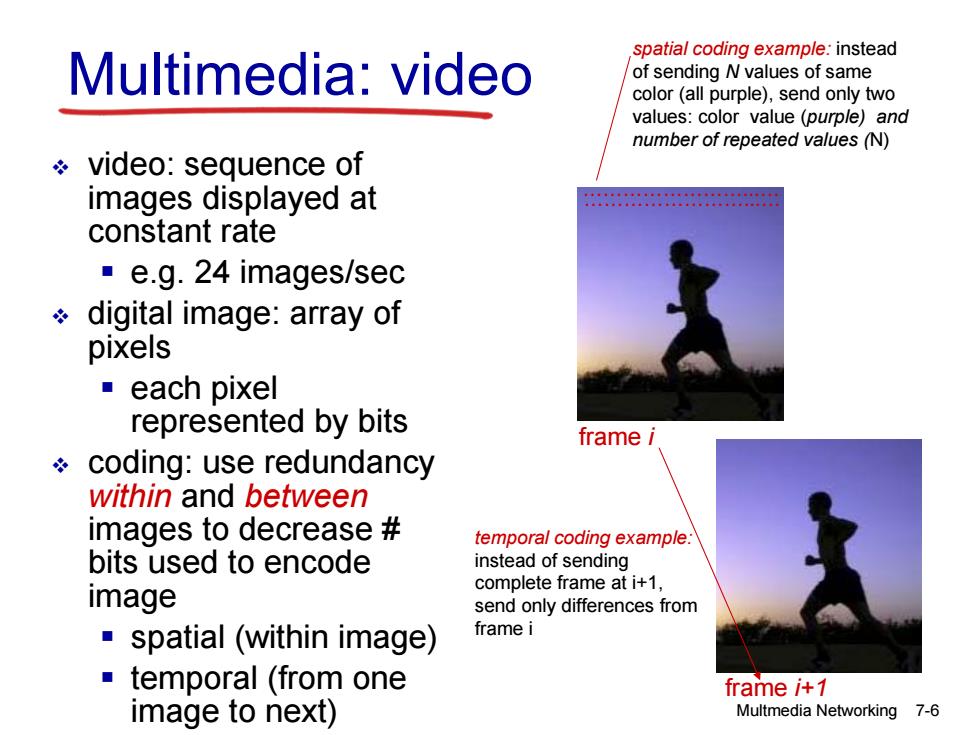
spatial coding example:instead Multimedia:video of sending N values of same color (all purple),send only two values:color value (purple)and number of repeated values(N) video:sequence of images displayed at 889888899838 constant rate ·e.g.24 images/sec digital image:array of pixels ■each pixel represented by bits frame i coding:use redundancy within and between images to decrease temporal coding example. bits used to encode instead of sending complete frame at i+1, image send only differences from spatial (within image) frame i temporal (from one frame i+1 image to next) Multmedia Networking 7-6
video: sequence of images displayed at constant rate e.g. 24 images/sec digital image: array of pixels each pixel represented by bits coding: use redundancy within and between images to decrease # bits used to encode image spatial (within image) temporal (from one image to next) Multmedia Networking 7-6 Multimedia: video ……………………...… spatial coding example: instead of sending N values of same color (all purple), send only two values: color value (purple) and number of repeated values (N) ……………………...… frame i frame i+1 temporal coding example: instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i
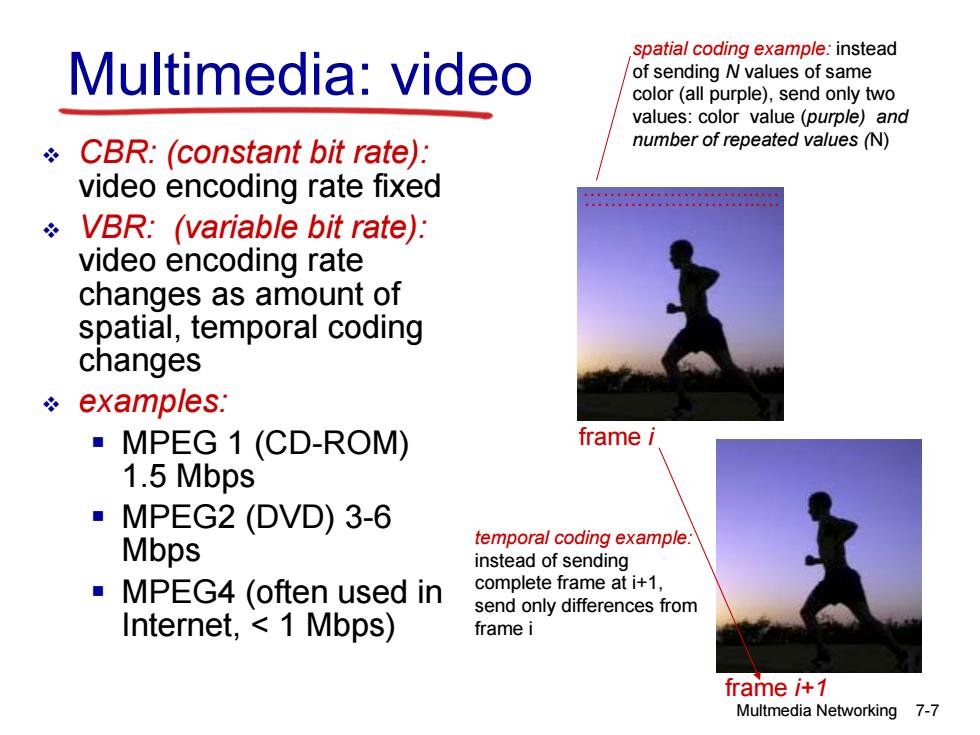
spatial coding example:instead Multimedia:video of sending N values of same color(all purple),send only two values:color value (purple)and CBR:(constant bit rate): number of repeated values (N) video encoding rate fixed 2080088002800 VBR:(variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial,temporal coding changes examples: ■MPEG1(CD-ROM) frame i 1.5 Mbps ·MPEG2(DVD)3-6 Mbps temporal coding example. instead of sending ■MPEG4(often used in complete frame at i+1. send only differences from Internet,1 Mbps) frame i frame i+1 Multmedia Networking 7-7
Multmedia Networking 7-7 Multimedia: video ……………………...… spatial coding example: instead of sending N values of same color (all purple), send only two values: color value (purple) and number of repeated values (N) ……………………...… frame i frame i+1 temporal coding example: instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i CBR: (constant bit rate): video encoding rate fixed VBR: (variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes examples: MPEG 1 (CD-ROM) 1.5 Mbps MPEG2 (DVD) 3-6 Mbps MPEG4 (often used in Internet, < 1 Mbps)

Multimedia networking:3 application types streaming,stored audio,video streaming:can begin playout before downloading entire file stored (at server):can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) e.g.,YouTube,Netflix,Hulu conversational voice/video over IP interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance e.g.,Skype streaming live audio,video e.g.,live sporting event (futbol) Multmedia Networking 7-8
Multimedia networking: 3 application types Multmedia Networking 7-8 streaming, stored audio, video streaming: can begin playout before downloading entire file stored (at server): can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) e.g., YouTube, Netflix, Hulu conversational voice/video over IP interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance e.g., Skype streaming live audio, video e.g., live sporting event (futbol)

Multimedia networking:outline 7.1 multimedia networking applications 7.2 streaming stored video 7.3 voice-over-IP 7.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 7.5 network support for multimedia Multmedia Networking 7-9
Multimedia networking: outline 7.1 multimedia networking applications 7.2 streaming stored video 7.3 voice-over-IP 7.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 7.5 network support for multimedia Multmedia Networking 7-9
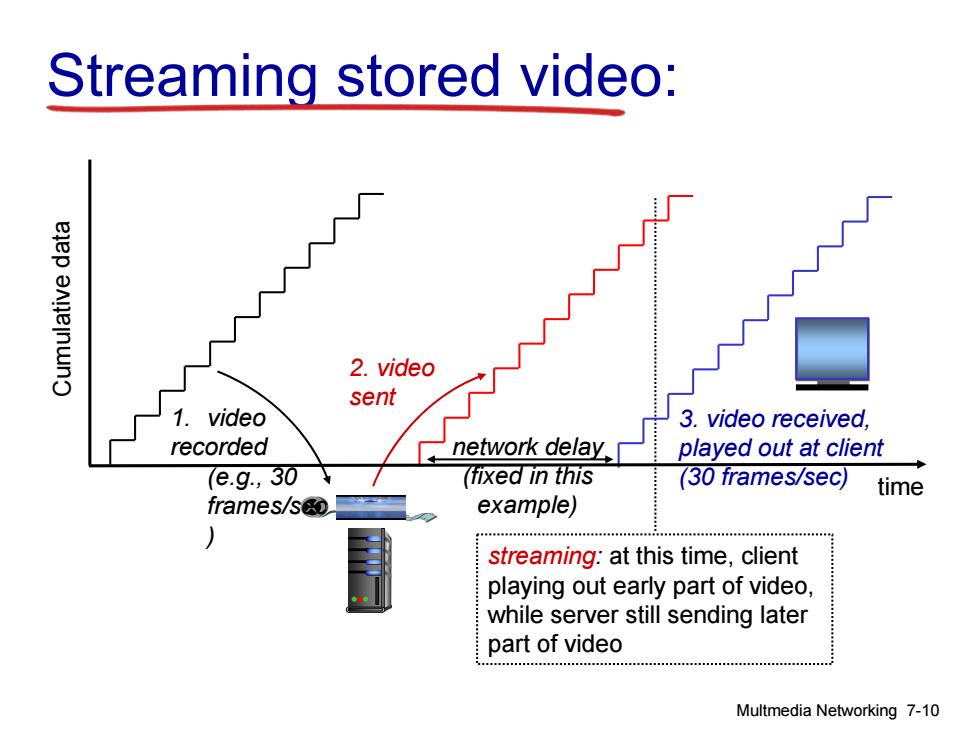
Streaming stored video: ejep anneinwno 2.video sent 1.video 3.video received, recorded network delay played out at client e.g.,30 (fixed in this (30 frames/sec) time frames/so example) streaming:at this time,client playing out early part of video. while server still sending later part of video Multmedia Networking 7-10
Streaming stored video: 1. video recorded (e.g., 30 frames/sec ) 2. video Csent umu al tive da at streaming: at this time, client playing out early part of video, while server still sending later part of video network delay (fixed in this example) time Multmedia Networking 7-10 3. video received, played out at client (30 frames/sec)