Representation of Geometric Information (Cont.) Representation of points and line segment in 3-D similar to 2-D,except that points have an extra z component Represent arbitrary polyhedra by dividing them into tetrahedrons,like triangulating polygons. Alternative:List their faces,each of which is a polygon,along with an indication of which side of the face is inside the polyhedron. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 25.12 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 25.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Representation of Geometric Information (Cont.) Representation of points and line segment in 3-D similar to 2-D, except that points have an extra z component Represent arbitrary polyhedra by dividing them into tetrahedrons, like triangulating polygons. Alternative: List their faces, each of which is a polygon, along with an indication of which side of the face is inside the polyhedron

Design Databases Represent design components as objects(generally geometric objects);the connections between the objects indicate how the design is structured. Simple two-dimensional objects:points,lines,triangles,rectangles, polygons. Complex two-dimensional objects:formed from simple objects via union,intersection,and difference operations. Complex three-dimensional objects:formed from simpler objects such as spheres,cylinders,and cuboids,by union,intersection, and difference operations. Wireframe models represent three-dimensional surfaces as a set of simpler objects. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 25.13 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 25.13 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Design Databases Represent design components as objects (generally geometric objects); the connections between the objects indicate how the design is structured. Simple two-dimensional objects: points, lines, triangles, rectangles, polygons. Complex two-dimensional objects: formed from simple objects via union, intersection, and difference operations. Complex three-dimensional objects: formed from simpler objects such as spheres, cylinders, and cuboids, by union, intersection, and difference operations. Wireframe models represent three-dimensional surfaces as a set of simpler objects
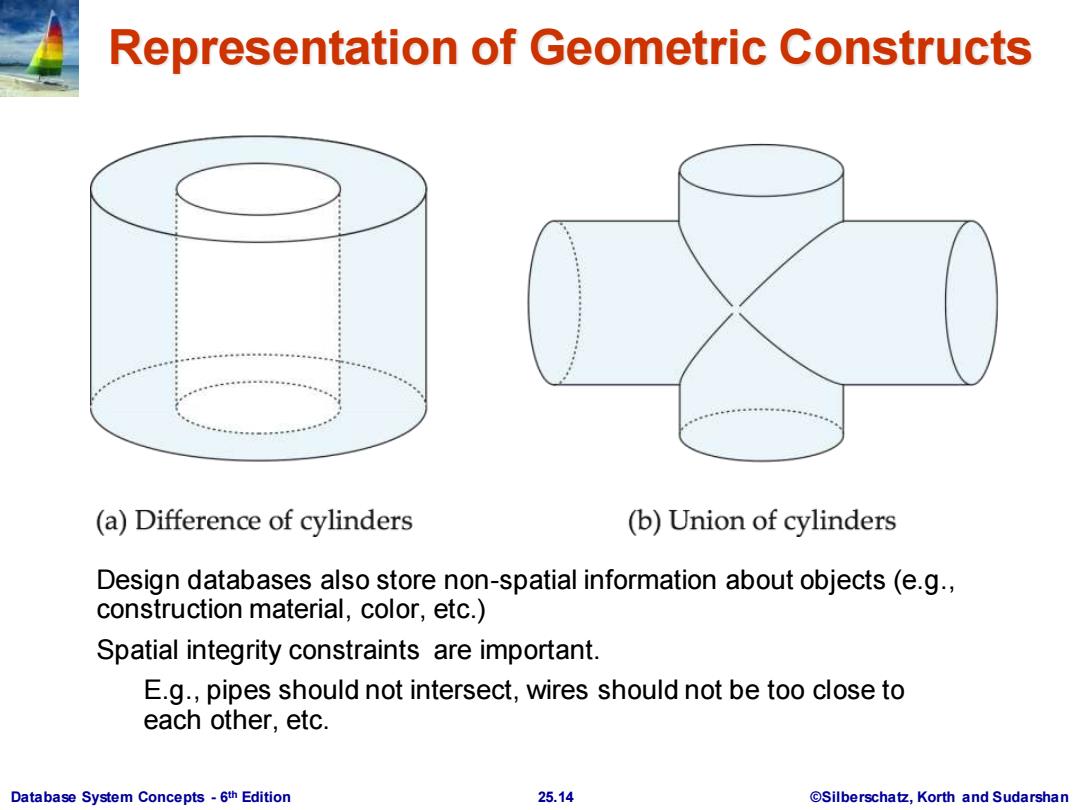
Representation of Geometric Constructs (a)Difference of cylinders (b)Union of cylinders Design databases also store non-spatial information about objects (e.g., construction material,color,etc.) Spatial integrity constraints are important. E.g.,pipes should not intersect,wires should not be too close to each other,etc. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 25.14 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 25.14 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Representation of Geometric Constructs Design databases also store non-spatial information about objects (e.g., construction material, color, etc.) Spatial integrity constraints are important. E.g., pipes should not intersect, wires should not be too close to each other, etc
Geographic Data Raster data consist of bit maps or pixel maps,in two or more dimensions. Example 2-D raster image:satellite image of cloud cover, where each pixel stores the cloud visibility in a particular area. Additional dimensions might include the temperature at different altitudes at different regions,or measurements taken at different points in time. Design databases generally do not store raster data. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 25.15 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 25.15 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Geographic Data Raster data consist of bit maps or pixel maps, in two or more dimensions. Example 2-D raster image: satellite image of cloud cover, where each pixel stores the cloud visibility in a particular area. Additional dimensions might include the temperature at different altitudes at different regions, or measurements taken at different points in time. Design databases generally do not store raster data
Geographic Data (Cont.) Vector data are constructed from basic geometric objects:points,line segments,triangles,and other polygons in two dimensions,and cylinders,spheres,cuboids,and other polyhedrons in three dimensions. Vector format often used to represent map data. Roads can be considered as two-dimensional and represented by lines and curves. Some features,such as rivers,may be represented either as complex curves or as complex polygons,depending on whether their width is relevant. Features such as regions and lakes can be depicted as polygons. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 25.16 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 25.16 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Geographic Data (Cont.) Vector data are constructed from basic geometric objects: points, line segments, triangles, and other polygons in two dimensions, and cylinders, spheres, cuboids, and other polyhedrons in three dimensions. Vector format often used to represent map data. Roads can be considered as two-dimensional and represented by lines and curves. Some features, such as rivers, may be represented either as complex curves or as complex polygons, depending on whether their width is relevant. Features such as regions and lakes can be depicted as polygons