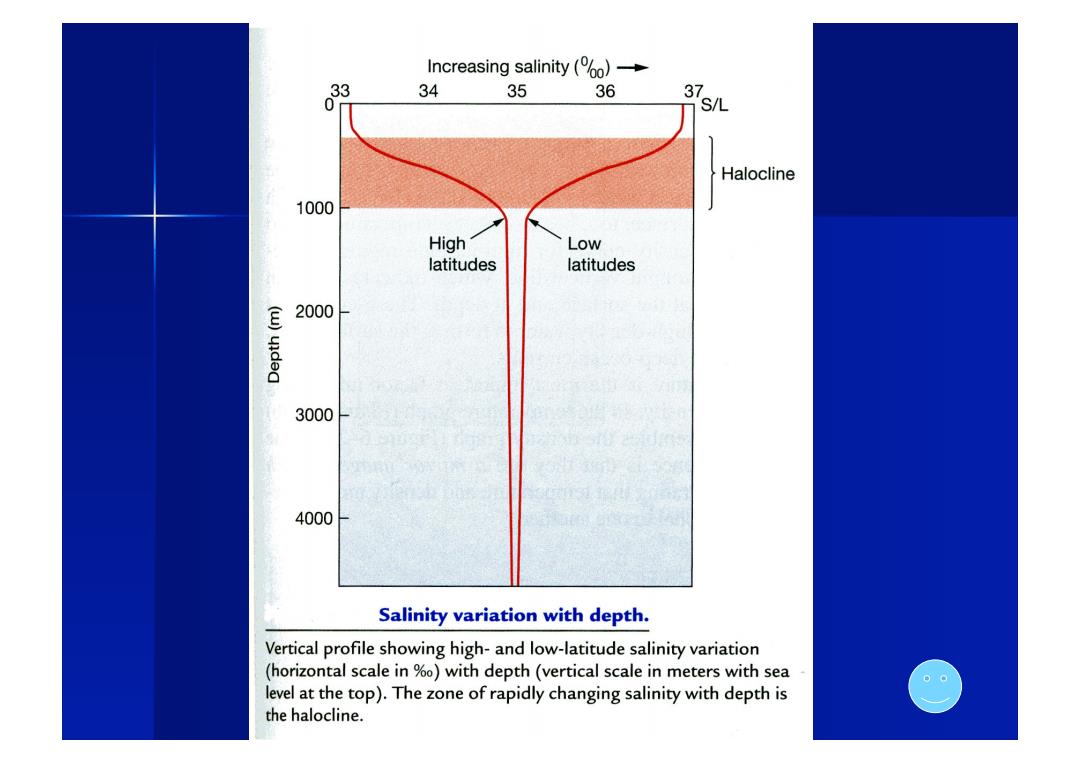
Increasing salinity (% 34 35 36 31 gL Halocline 1000 High Low latitudes latitudes E 2000 3000 4000 Salinity variation with depth. Vertical profile showing high-and low-latitude salinity variation (horizontal scale in %0)with depth(vertical scale in meters with sea 00 level at the top).The zone of rapidly changing salinity with depth is the halocline
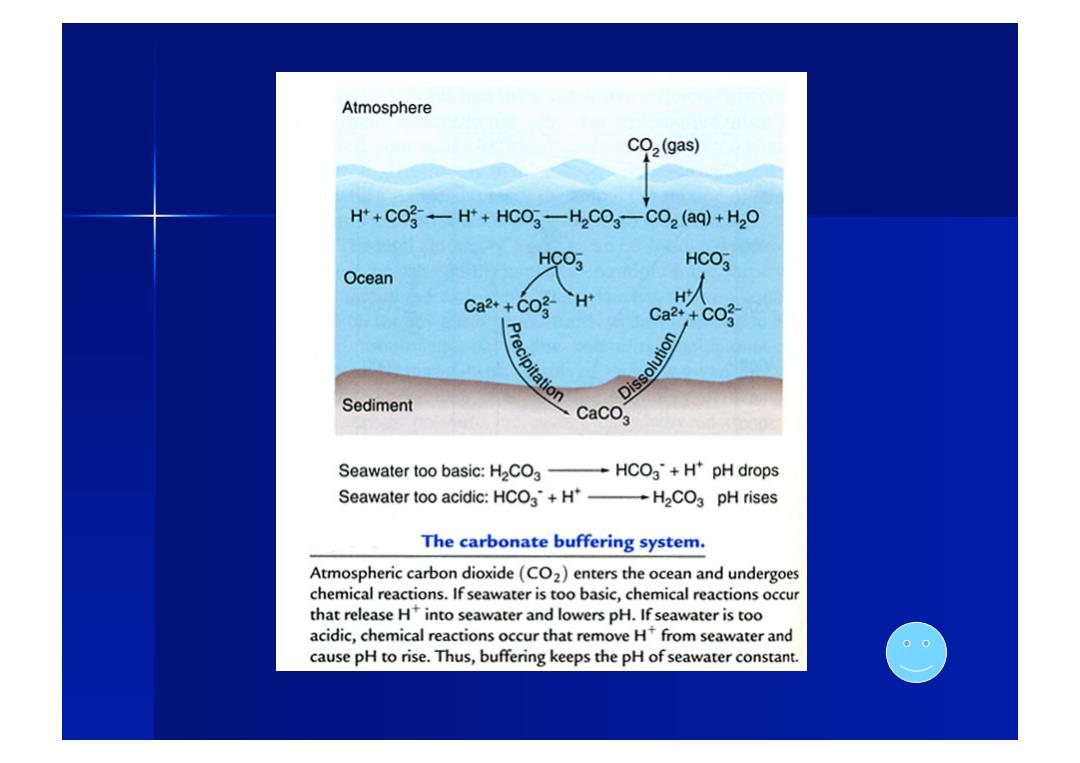
Atmosphere CO2(gas) H++CO-H*+HCO3-H2CO3-CO2(aq)+H2O HCO3 HCO3 Ocean Ca2++CO- H H人 Ca2+CO Dissolution Sediment CaCO3 Seawater too basic:H2CO3-HCO3+H*pH drops Seawater too acidic:HCO3+H*-H2CO3 pH rises The carbonate buffering system. Atmospheric carbon dioxide(CO2)enters the ocean and undergoes chemical reactions.If seawater is too basic,chemical reactions occur that release H into seawater and lowers pH.If seawater is too acidic,chemical reactions occur that remove Hfrom seawater and cause pH to rise.Thus,buffering keeps the pH of seawater constant
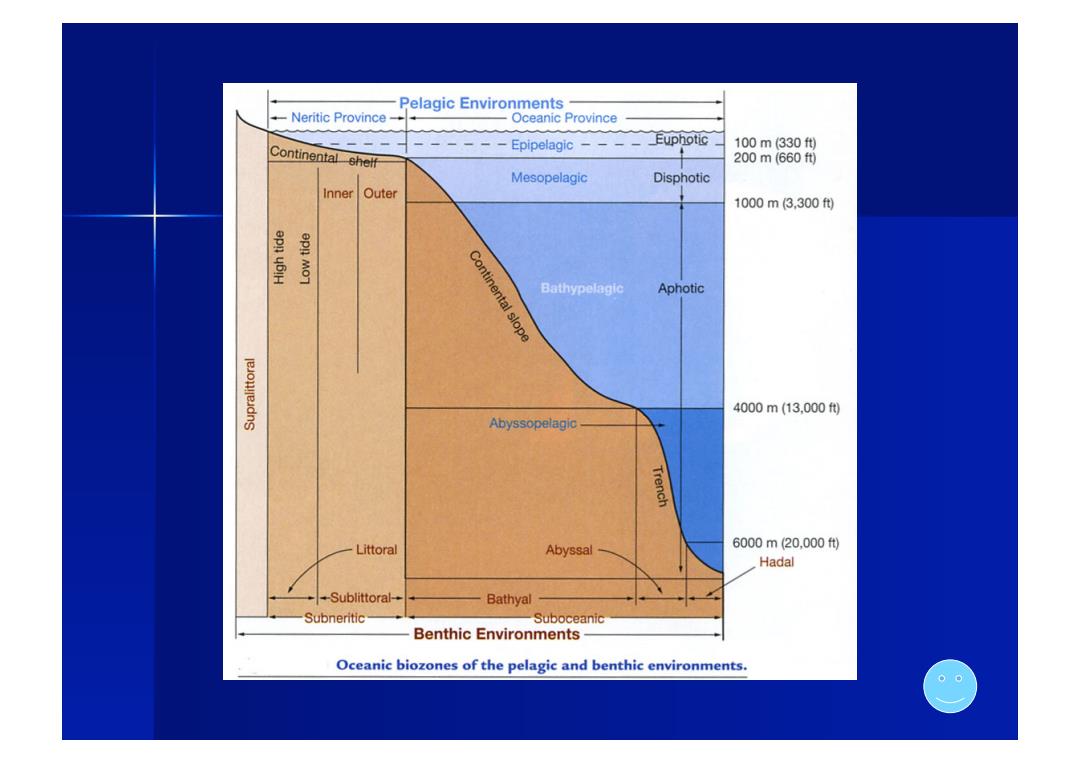
Pelagic Environments Neritic Province Oceanic Province Euphotic 、 100m330ft) Continentalshelf Epipelagic 200m(660f0) Mesopelagic Disphotic Inner Outer 1000m3,300f倒 epn MoT Continental slope Bathypelagic Aphotic 4000m(13,000) Abyssopelagic Trench Littoral Abyssal 6000m20,000) Hadal -Sublittoral- Bathyal Subneritic Suboceanic Benthic Environments Oceanic biozones of the pelagic and benthic environments
Lecturel.2海洋生境
