Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) ■unique“code”assigned to each user;i.e.,code set partitioning all users share same frequency,but each user has own "chipping"sequence (i.e.,code)to encode data allows multiple users to "coexist"and transmit simultaneously with minimal interference (if codes are orthogonal) encoded signal (original data)X(chipping sequence) decoding:inner-product of encoded signal and chipping sequence Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-16
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) ▪ unique “code” assigned to each user; i.e., code set partitioning • all users share same frequency, but each user has own “chipping” sequence (i.e., code) to encode data • allows multiple users to “coexist” and transmit simultaneously with minimal interference (if codes are “orthogonal”) ▪ encoded signal = (original data) X (chipping sequence) ▪ decoding: inner-product of encoded signal and chipping sequence Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-16
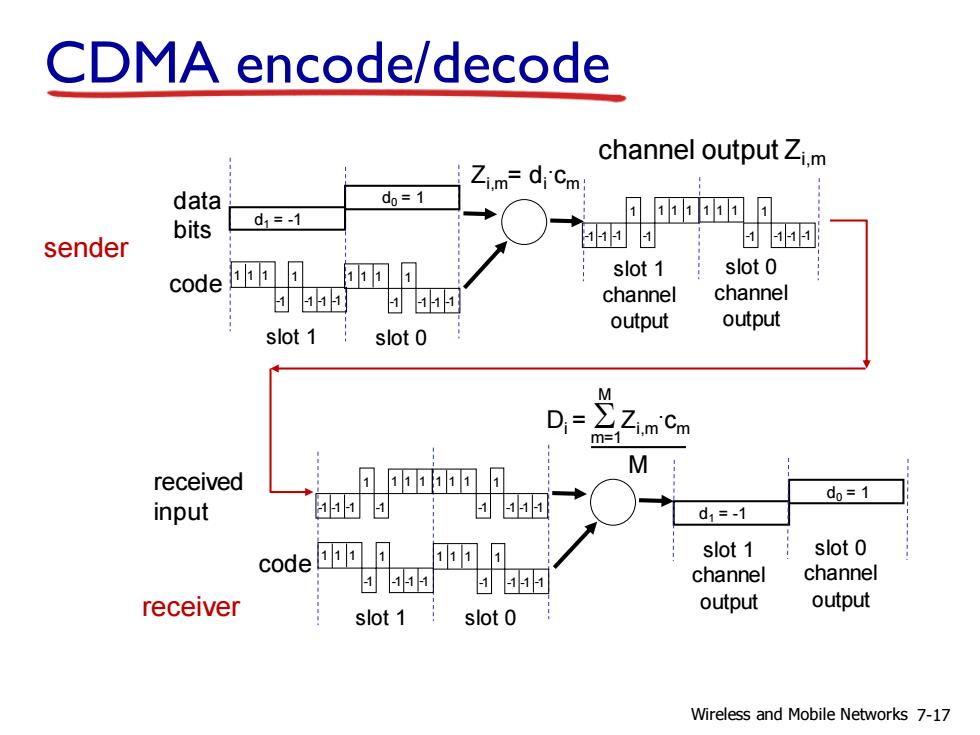
CDMA encode/decode channel output Zi.m Zi.m=di'Cm: data d0=1 d1=-1 0可可 bits sender 的 5HH code 可可 11可 slot 1 slot 0 色中 channel channel output output slot 1 slot0 D= M received 55 d0=1 input d1=-1 slot 1 slot 0 code 1币可 1同 的5 色5 channel channel receiver output output slot 1 slot 0 Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-17
CDMA encode/decode slot 1 slot 0 d1 = -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 Zi,m= di . cm d0 = 1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 slot 0 channel output slot 1 channel output channel output Zi,m sender code data bits slot 1 slot 0 d1 = -1 d0 = 1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 slot 0 channel output slot 1 channel output receiver code received input Di = S Zi,m . cm m=1 M M Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-17
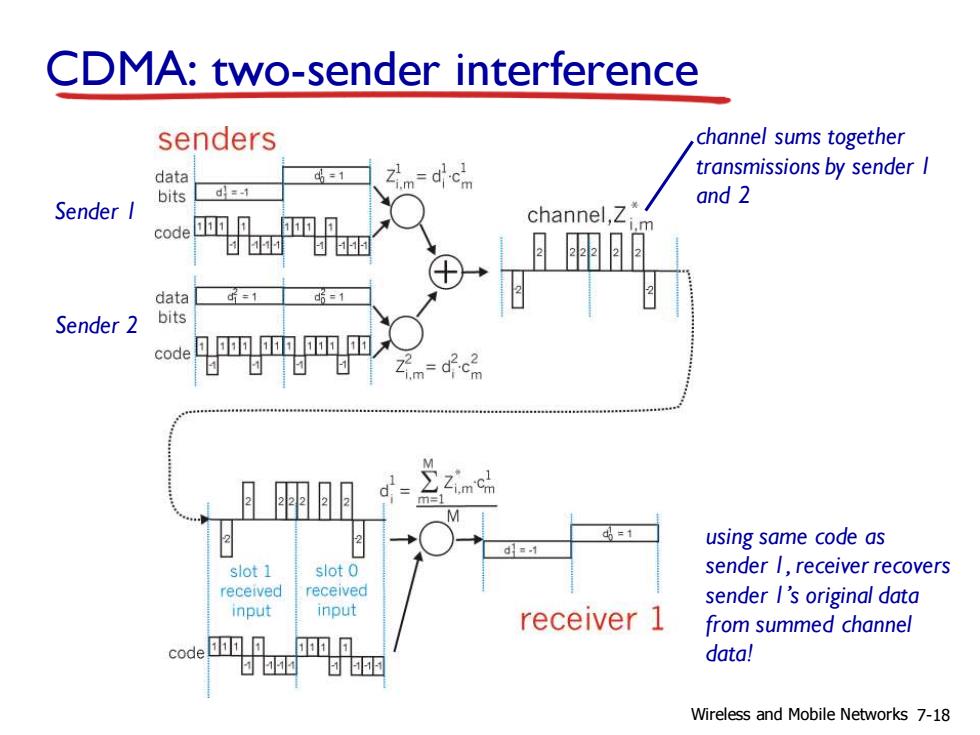
CDMA:two-sender interference senders channel sums together data =1 Zim-dcm transmissions by sender I bits d=-1 and 2 Sender I 匝可 channel,Z code data d=1 =1 Sender 2 bits code 见匝匝匝匝入 mc using same code as slot 1 slot 0 sender I,receiver recovers received received sender I's original data input input receiver 1 from summed channel code匝匝日 币可 data! Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-18
CDMA: two-sender interference using same code as sender 1, receiver recovers sender 1’s original data from summed channel data! Sender 1 Sender 2 channel sums together transmissions by sender 1 and 2 Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-18
Chapter 7 outline 7.I Introduction Mobility Wireless 7.5 Principles:addressing and routing to mobile users 7.2 Wireless links, characteristics 7.6 Mobile IP ·CDMA 7.7 Handling mobility in 7.3 IEEE 802.I I wireless cellular networks LANs(“Wi-Fi”) 7.8 Mobility and higher-layer 7.4 Cellular Internet Access protocols ·architecture standards(e.g.,3G,LTE) Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-19
Chapter 7 outline 7.1 Introduction Wireless 7.2 Wireless links, characteristics • CDMA 7.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs (“Wi-Fi”) 7.4 Cellular Internet Access • architecture • standards (e.g., 3G, LTE) Mobility 7.5 Principles: addressing and routing to mobile users 7.6 Mobile IP 7.7 Handling mobility in cellular networks 7.8 Mobility and higher-layer protocols Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-19
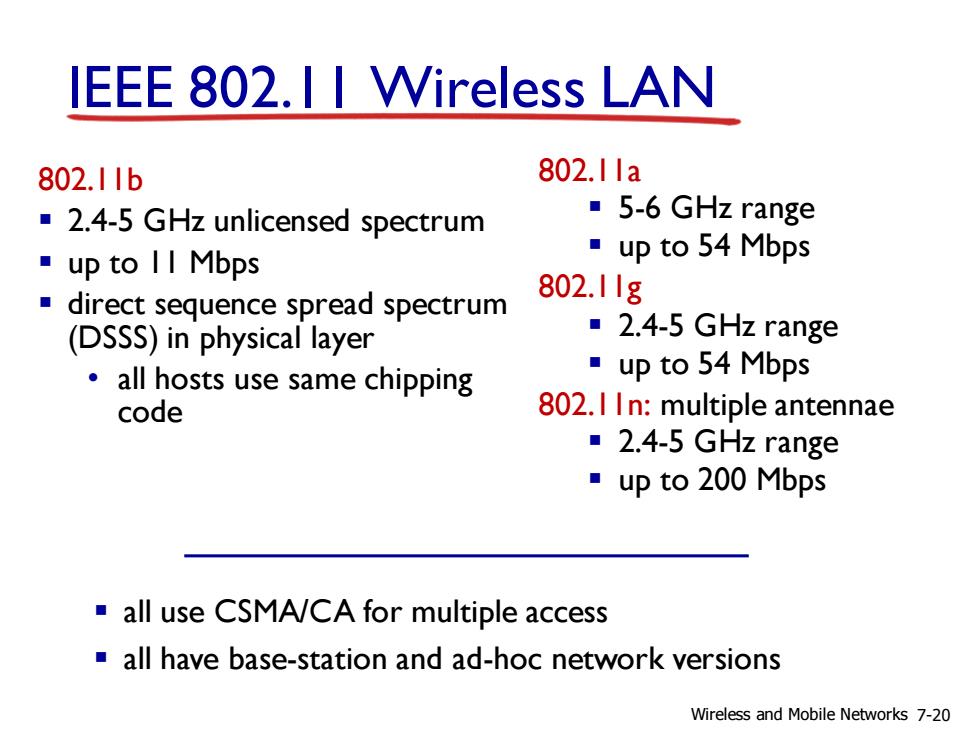
IEEE 802.II Wireless LAN 802.1Ib 802.1la 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed spectrum ·5-6 GHz range ·up to II Mbps ·upto54Mbps direct sequence spread spectrum 802.11g (DSSS)in physical layer ■2.4-5 GHz range all hosts use same chipping ·upto54Mbps code 802.I In:multiple antennae ■2.4-5 GHz range ·upto200Mbps all use CSMA/CA for multiple access all have base-station and ad-hoc network versions Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-20
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN 802.11b ▪ 2.4-5 GHz unlicensed spectrum ▪ up to 11 Mbps ▪ direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) in physical layer • all hosts use same chipping code 802.11a ▪ 5-6 GHz range ▪ up to 54 Mbps 802.11g ▪ 2.4-5 GHz range ▪ up to 54 Mbps 802.11n: multiple antennae ▪ 2.4-5 GHz range ▪ up to 200 Mbps ▪ all use CSMA/CA for multiple access ▪ all have base-station and ad-hoc network versions Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-20