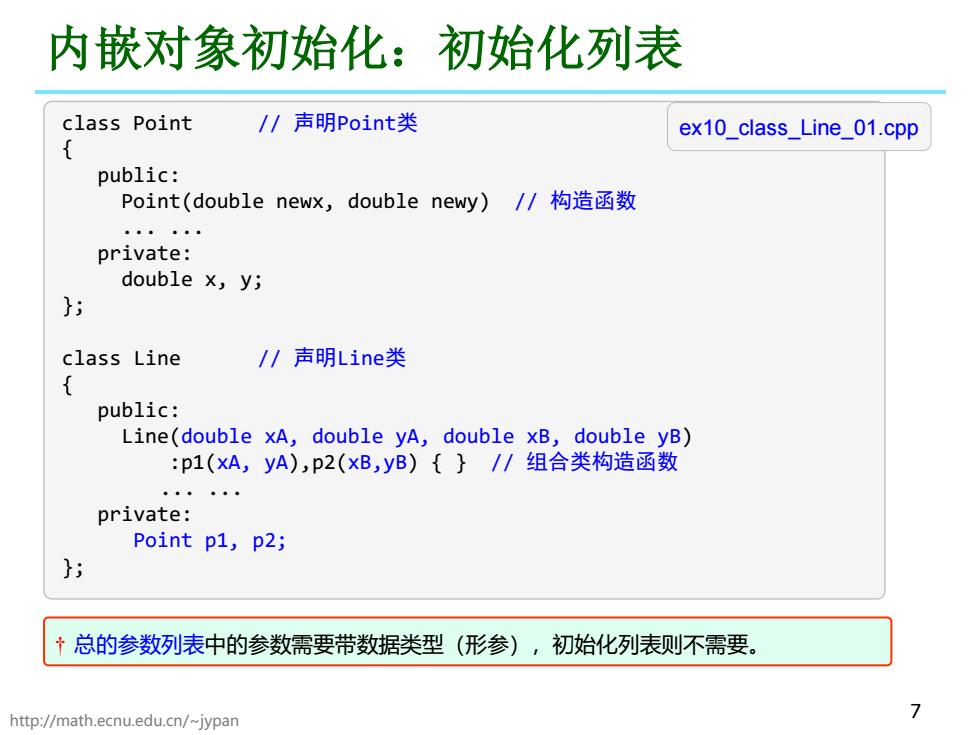
内嵌对象初始化:初始化列表 class Point //声明Point类 ex10_class_Line_01.cpp public: Point(double newx,double newy) /1构造函数 private: double x,y; } class Line /声明Line类 public: Line(double xA,double yA,double xB,double yB) :p1(xA,yA),p2(xB,yB){}/I组合类构造函数 private: Point p1,p2; 总的参数列表中的参数需要带数据类型(形参),初始化列表则不需要。 http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan
http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 7 内嵌对象初始化:初始化列表 class Point // 声明Point类 { public: Point(double newx, double newy) // 构造函数 ... ... private: double x, y; }; class Line // 声明Line类 { public: Line(double xA, double yA, double xB, double yB) :p1(xA, yA),p2(xB,yB) { } // 组合类构造函数 ... ... private: Point p1, p2; }; ex10_class_Line_01.cpp † 总的参数列表中的参数需要带数据类型(形参),初始化列表则不需要
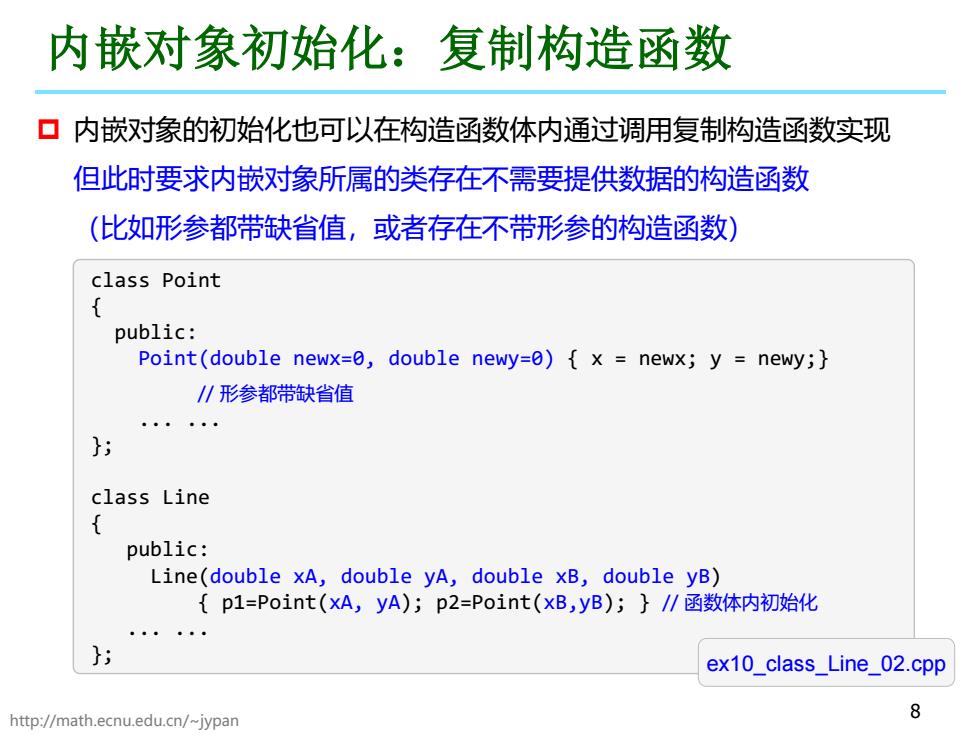
内嵌对象初始化:复制构造函数 口内嵌对象的初始化也可以在构造函数体内通过调用复制构造函数实现 但此时要求内嵌对象所属的类存在不需要提供数据的构造函数 (比如形参都带缺省值,或者存在不带形参的构造函数) class Point public: Point(double newx=0,double newy=0){x newx;y newy;} 川形参都带缺省值 ····· }; class Line public: Line(double xA,double yA,double xB,double yB) {p1=Point(A,yA);p2=Point(xB,yB);}∥函数体内初始化 ex10 class Line_02.cpp http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/-jypan
http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 8 内嵌对象初始化:复制构造函数 class Point { public: Point(double newx=0, double newy=0) { x = newx; y = newy;} // 形参都带缺省值 ... ... }; class Line { public: Line(double xA, double yA, double xB, double yB) { p1=Point(xA, yA); p2=Point(xB,yB); } // 函数体内初始化 ... ... }; ex10_class_Line_02.cpp 内嵌对象的初始化也可以在构造函数体内通过调用复制构造函数实现 但此时要求内嵌对象所属的类存在不需要提供数据的构造函数 (比如形参都带缺省值,或者存在不带形参的构造函数)

内嵌对象初始化:复制构造函数 class Point public: Point(){x=;y=;}/∥存在不带形参的构造函数 Point(double newx,double newy){x newx;y newy;} } class Line public: Line(Point&A,Poin&B){pl=A;p2=B;}∥函数体内初始化 } ex10 class_Line_03.cpp http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 9
http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 9 内嵌对象初始化:复制构造函数 class Point { public: Point() {x = 0; y = 0;} // 存在不带形参的构造函数 Point(double newx, double newy) { x = newx; y = newy;} ... ... }; class Line { public: Line(Point & A, Poin & B) { p1=A; p2=B; } // 函数体内初始化 ... ... }; ex10_class_Line_03.cpp
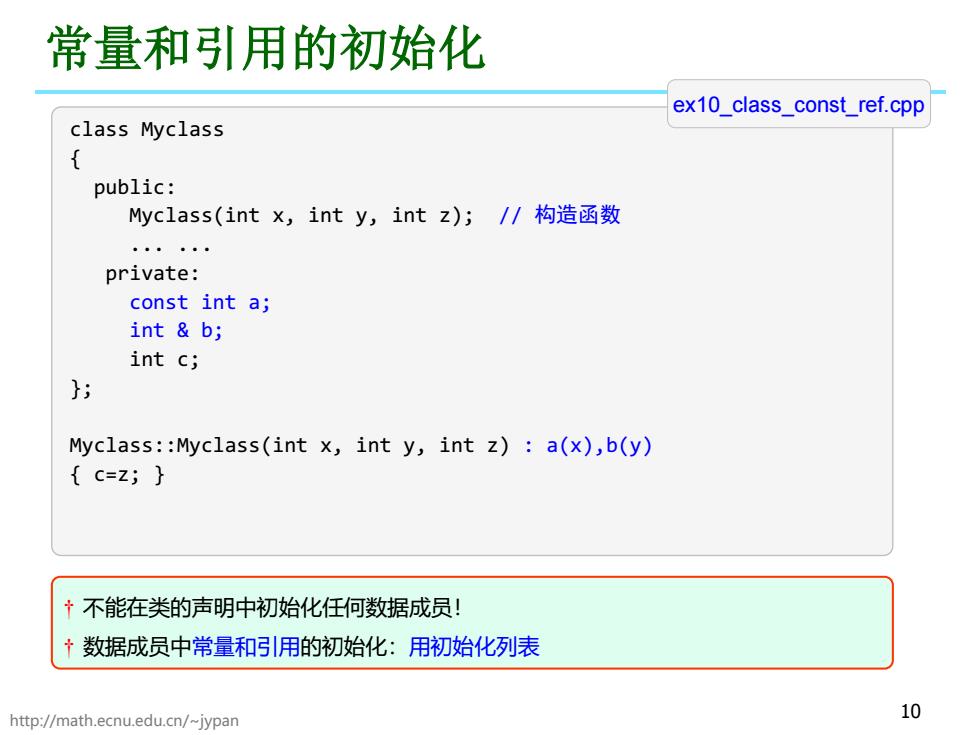
常量和引用的初始化 ex10_class_const_ref.cpp class Myclass { public: lyclass(intx,inty,intz);/构造函数 。·。。。。 private: const int a; int b; int c; Myclass:Myclass(int x,int y,int z):a(x),b(y) {c=z;} 不能在类的声明中初始化任何数据成员! ↑数据成员中常量和引用的初始化:用初始化列表 http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 10
http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 10 常量和引用的初始化 class Myclass { public: Myclass(int x, int y, int z); // 构造函数 ... ... private: const int a; int & b; int c; }; Myclass::Myclass(int x, int y, int z) : a(x),b(y) { c=z; } ex10_class_const_ref.cpp † 不能在类的声明中初始化任何数据成员! † 数据成员中常量和引用的初始化:用初始化列表

前向引用声明 ·类必须先定义后使用 ●若两个类互相引用,则需要使用前向引用声明 Example class ClassB; /前向引用声明 class classA /声明A类 { public: void f(ClassB b); } class ClassB //声明B类 public: void g(ClassA a); 使用前向引用声明时,只能使用被声明的符号,而不能涉及类的任何细节。 http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 11
http://math.ecnu.edu.cn/~jypan 11 前向引用声明 类必须先定义后使用 若两个类互相引用,则需要使用前向引用声明 class ClassB; // 前向引用声明 class ClassA // 声明 A 类 { public: void f(ClassB b); }; class ClassB // 声明 B 类 { public: void g(ClassA a); }; † 使用前向引用声明时,只能使用被声明的符号,而不能涉及类的任何细节。 Example