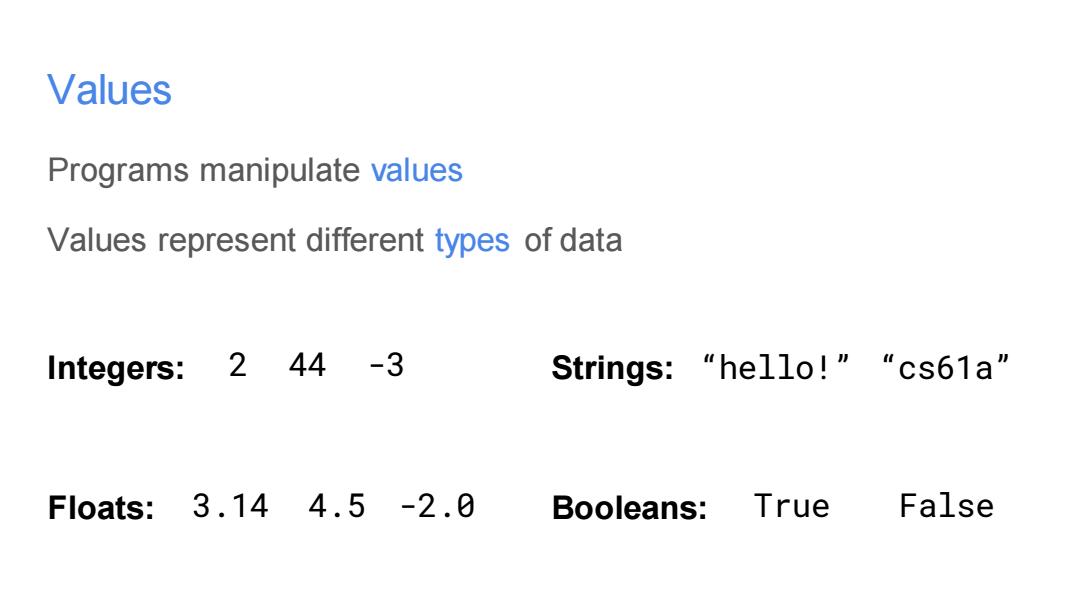
Values Programs manipulate values Values represent different types of data Integers:2 44-3 Strings:“hello!”“cs61a” Floats:3.144.5-2.0 Booleans:True False
Values Programs manipulate values Values represent different types of data Floats: Integers: Strings: Booleans: 2 44 -3 3.14 4.5 -2.0 “hello!” “cs61a” True False

Expressions Values Expressions evaluate to values in one or more steps Expression: Value: he11o!' 'hello!' 7/2 3.5 add(1,max(2,3)) 4
Expressions & Values Expressions evaluate to values in one or more steps ‘hello!’ 7 / 2 3.5 add(1, max(2, 3)) 4 Expression: ‘hello!’ Value:
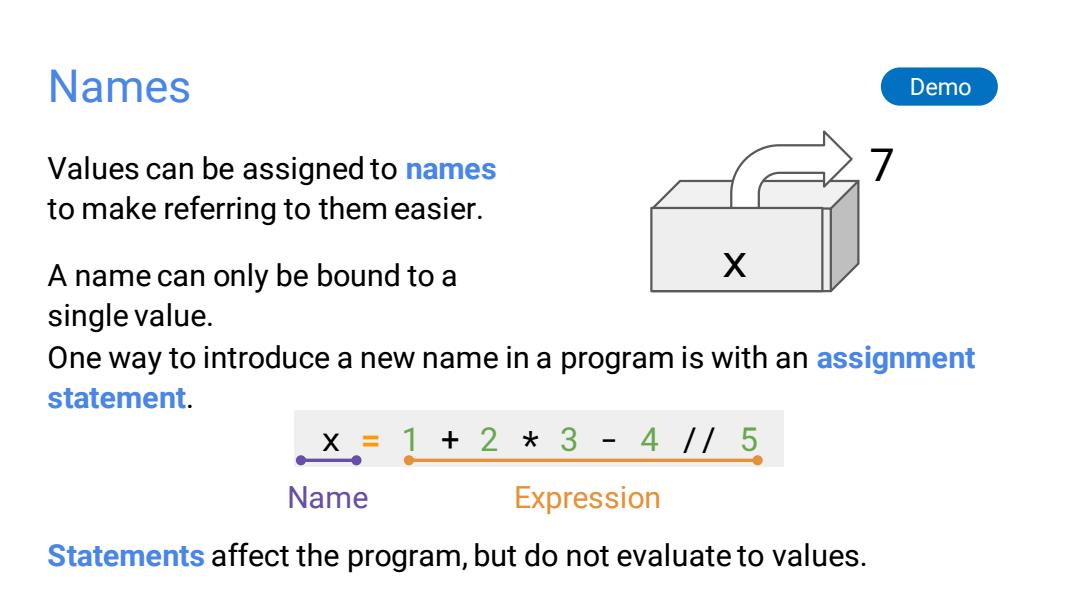
Names Demo Values can be assigned to names to make referring to them easier. A name can only be bound to a X single value. One way to introduce a new name in a program is with an assignment statement. ×=1+2*3-4//5 Name Expression Statements affect the program,but do not evaluate to values
Names Values can be assigned to names to make referring to them easier. A name can only be bound to a single value. Demo One way to introduce a new name in a program is with an assignment statement. x = 1 + 2 * 3 - 4 // 5 Name Expression 7 x Statements affect the program, but do not evaluate to values