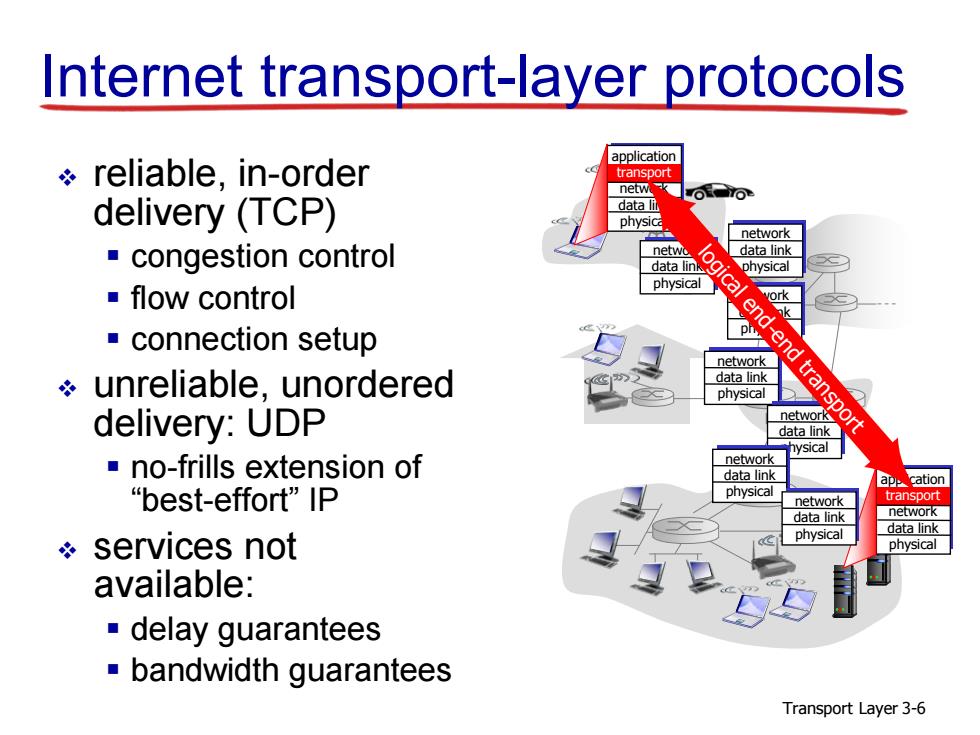
Internet transport-layer protocols application reliable,in-order transport netw delivery(TCP) data lu network congestion control data lin data link physical physical ■flow control ork connection setup ph network d unreliable,unordered data link physical ansp delivery:UDP network data link no-frills extension of network data link app cation “best-effort'”lP physical network transport data link network data link services not physical physical available: delay guarantees bandwidth guarantees Transport Layer 3-6
Transport Layer 3-6 Internet transport-layer protocols reliable, in-order delivery (TCP) congestion control flow control connection setup unreliable, unordered delivery: UDP no-frills extension of “best-effort” IP services not available: delay guarantees bandwidth guarantees application transport network data link physical application transport network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical logical end-end transport
Chapter 3 outline 3.1 transport-layer 3.5 connection-oriented services transport:TCP 3.2 multiplexing and segment structure demultiplexing -reliable data transfer 3.3 connectionless ■flow control transport:UDP connection 3.4 principles of management reliable data 3.6 principles of transfer congestion control 3.7 TCP congestion control Transport Layer 3-7
Transport Layer 3-7 Chapter 3 outline 3.1 transport-layer services 3.2 multiplexing and demultiplexing 3.3 connectionless transport: UDP 3.4 principles of reliable data transfer 3.5 connection-oriented transport: TCP segment structure reliable data transfer flow control connection management 3.6 principles of congestion control 3.7 TCP congestion control
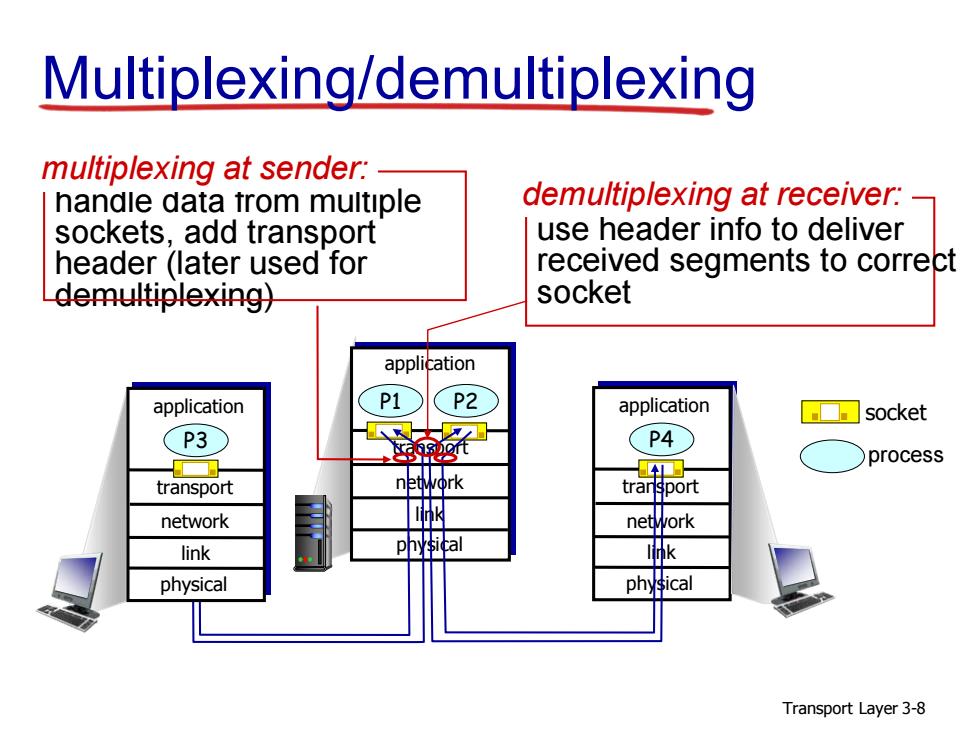
Multiplexing/demultiplexing multiplexing at sender: handle data trom muitiple demultiplexing at receiver: sockets,add transport use header info to deliver header (later used for received segments to correct demultiplexing) socket application application P1 P2 application ☐□socket (P3 (P4 process transport network transport network network link k physical physical Transport Layer 3-8
Transport Layer 3-8 Multiplexing/demultiplexing process socket use header info to deliver received segments to correct socket handle data from multiple demultiplexing at receiver: sockets, add transport header (later used for demultiplexing) multiplexing at sender: transport application physical link network P1 P2 transport application physical link network P4 transport application physical link network P3
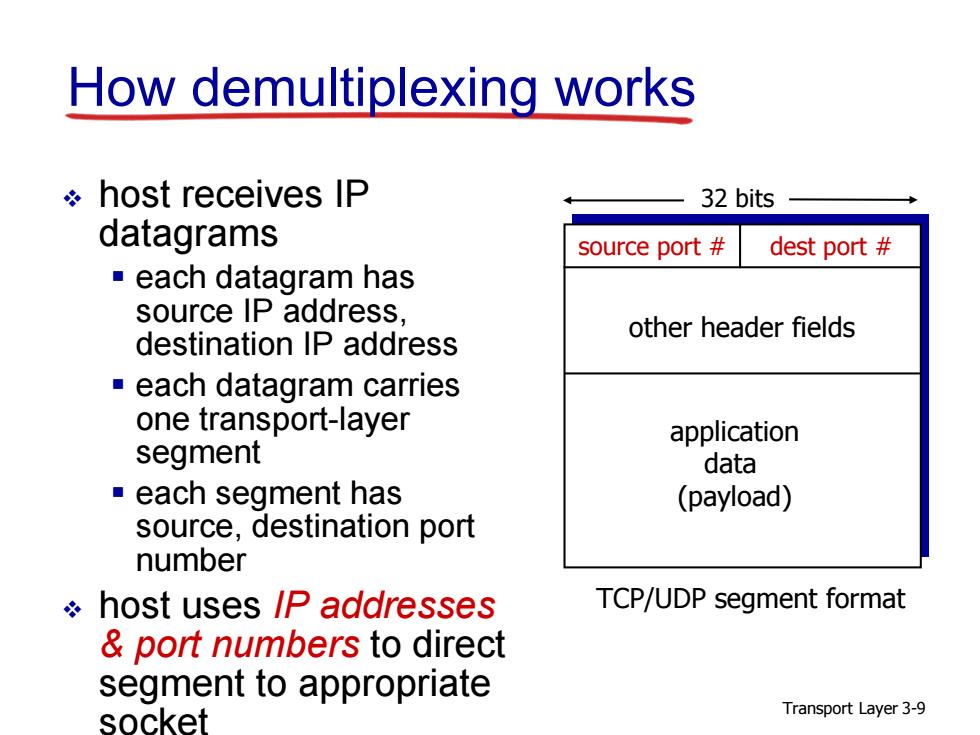
How demultiplexing works host receives IP 32 bits datagrams source port dest port each datagram has source IP address, other header fields destination IP address each datagram carries one transport-layer application segment data each segment has (payload) source,destination port number host uses IP addresses TCP/UDP segment format port numbers to direct segment to appropriate socket Transport Layer 3-9
Transport Layer 3-9 How demultiplexing works host receives IP datagrams each datagram has source IP address, destination IP address each datagram carries one transport-layer segment each segment has source, destination port number host uses IP addresses & port numbers to direct segment to appropriate soc ket source port # dest port # 32 bits application data (payload) other header fields TCP/UDP segment format
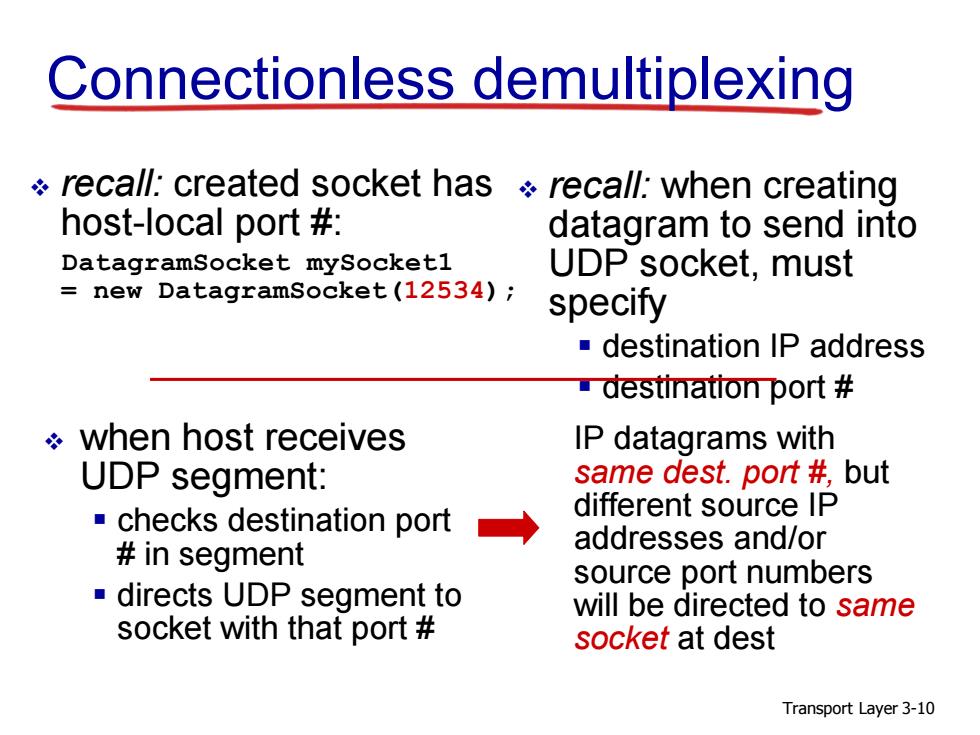
Connectionless demultiplexing recall:created socket has recall:when creating host-local port # datagram to send into DatagramSocket mySocketl UDP socket,must new DatagramSocket(12534); specify destination IP address destination port when host receives IP datagrams with UDP segment: same dest.port #but checks destination port different source IP in segment addresses and/or source port numbers -directs UDP segment to will be directed to same socket with that port socket at dest Transport Layer 3-10
Transport Layer 3-10 Connectionless demultiplexing recall: created socket has host-local port #: DatagramSocket mySocket1 = new DatagramSocket(12534); when host receives UDP segment: checks destination port # in segment directs UDP segment to socket with that port # recall: when creating datagram to send into UDP socket, must specify destination IP address destination port # IP datagrams with same dest. port #, but different source IP addresses and/or source port numbers will be directed to same socket at dest