Datagram networks no call setup at network layer routers:no state about end-to-end connections ■no network-level concept of“connection" packets forwarded using destination host address application application transport transport network 1.send datagrams 2.receive datagrams network data link data link physical physical Network Layer 4-16
Network Layer 4-16 Datagram networks no call setup at network layer routers: no state about end-to-end connections no network-level concept of “connection” packets forwarded using destination host address 1. send datagrams application transport network data link physical application transport network data link physical 2. receive datagrams
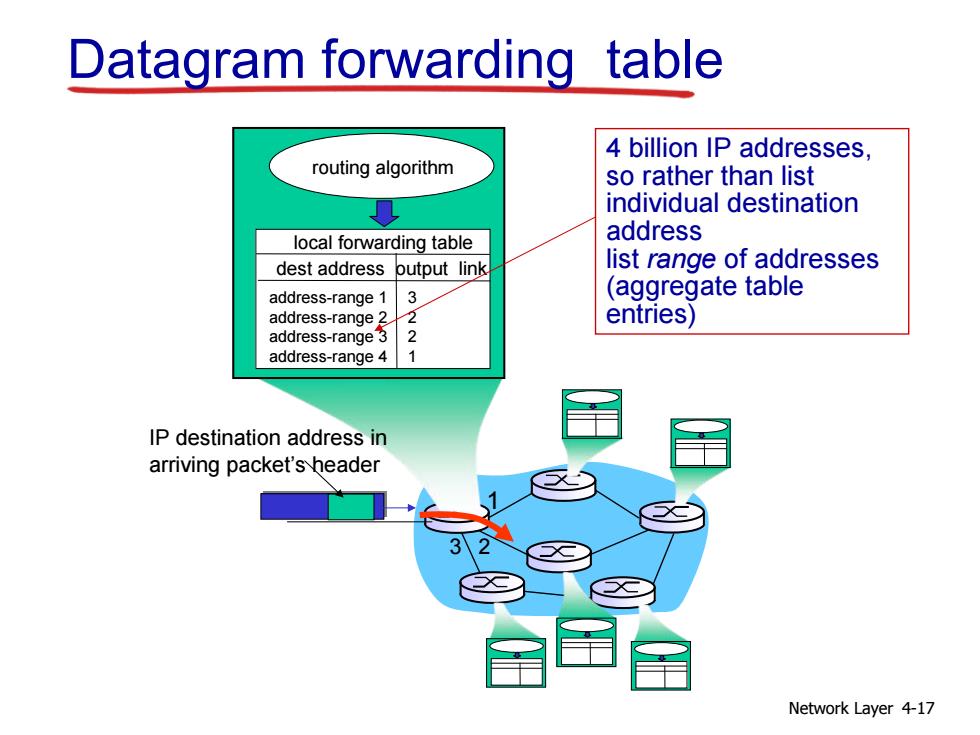
Datagram forwarding table 4 billion IP addresses, routing algorithm so rather than list individual destination local forwarding table address dest address butput link list range of addresses address-range 1 3 (aggregate table address-range 2 entries) address-range address-range 4 IP destination address in arriving packet's header Network Layer 4-17
Network Layer 4-17 1 3 2 Datagram forwarding table IP destination address in arriving packet’s header routing algorithm local forwarding table dest address output link address-range 1 address-range 2 address-range 3 address-range 4 3 2 2 1 4 billion IP addresses, so rather than list individual destination address list range of addresses (aggregate table entries)
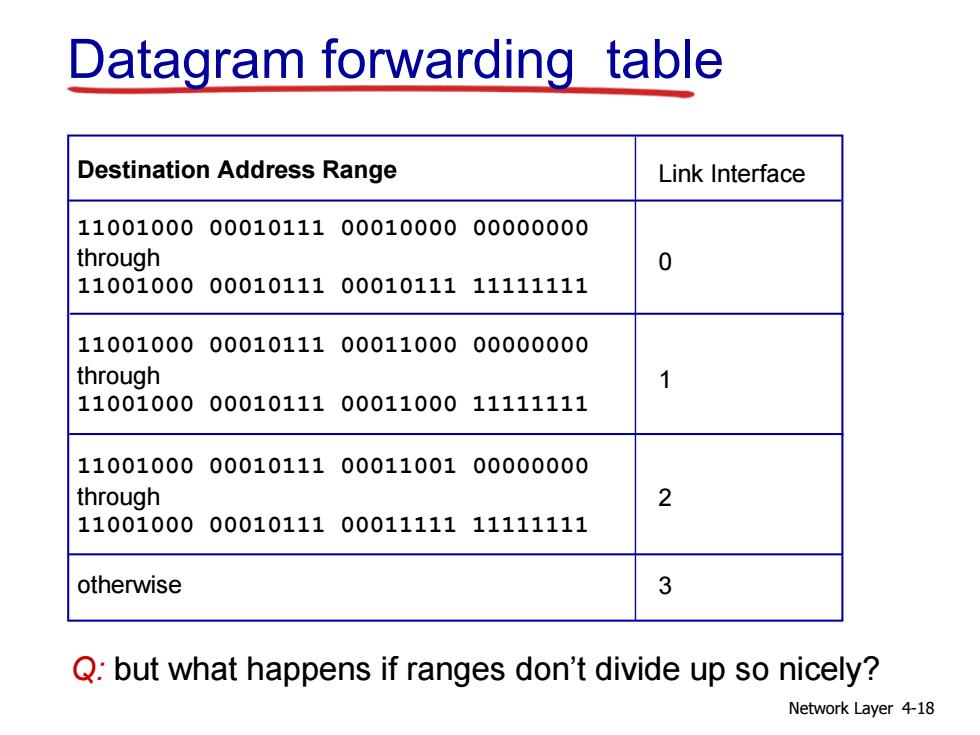
Datagram forwarding table Destination Address Range Link Interface 11001000000101110001000000000000 through 0 11001000000101110001011111111111 11001000000101110001100000000000 through 11001000000101110001100011111111 11001000000101110001100100000000 through 2 11001000000101110001111111111111 otherwise 3 Q:but what happens if ranges don't divide up so nicely? Network Layer 4-18
Network Layer 4-18 Destination Address Range 11001000 00010111 00010000 00000000 through 11001000 00010111 00010111 11111111 11001000 00010111 00011000 00000000 through 11001000 00010111 00011000 11111111 11001000 00010111 00011001 00000000 through 11001000 00010111 00011111 11111111 otherwise Link Interface 0 1 2 3 Q: but what happens if ranges don’t divide up so nicely? Datagram forwarding table
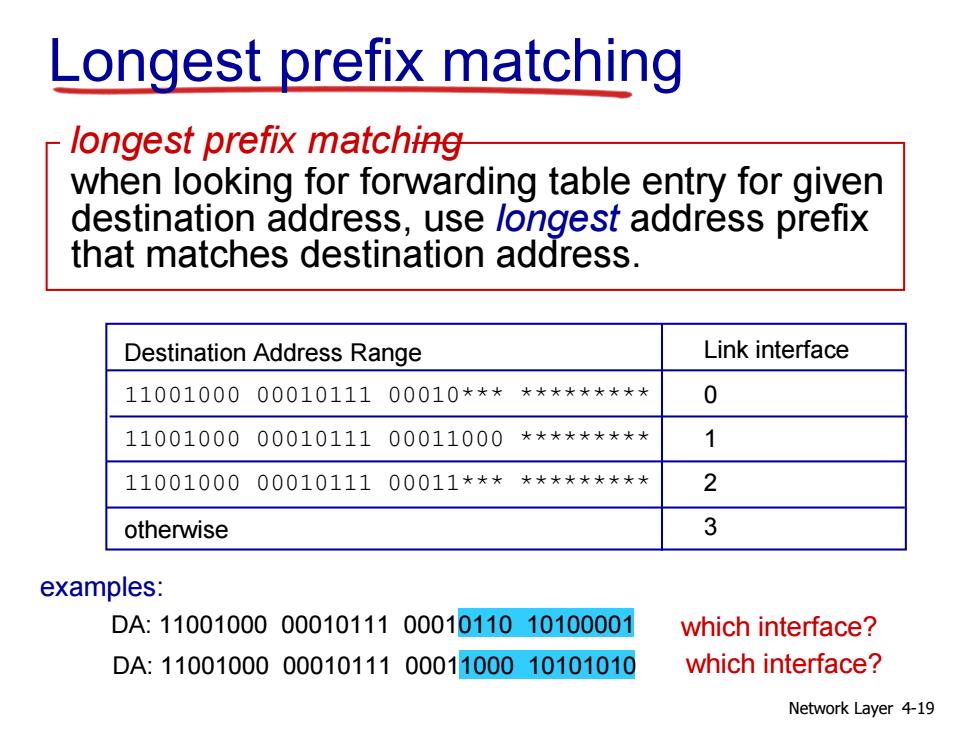
Longest prefix matching longest prefix matching when looking for forwarding table entry for given destination address,use longest address prefix that matches destination address. Destination Address Range Link interface 110010000001011100010************ 0 110010000001011100011000********* 1 110010000001011100011************ 2 otherwise 3 examples: DA:11001000000101110001011010100001 which interface? DA:11001000000101110001100010101010 which interface? Network Layer 4-19
Network Layer 4-19 Longest prefix matching Destination Address Range 11001000 00010111 00010*** ********* 11001000 00010111 00011000 ********* 11001000 00010111 00011*** ********* otherwise DA: 11001000 00010111 00011000 10101010 examples: DA: 11001000 00010111 00010110 10100001 which interface? which interface? when looking for forwarding table entry for given destination address, use longest address prefix that matches destination address. longest prefix matching Link interface 0 1 2 3
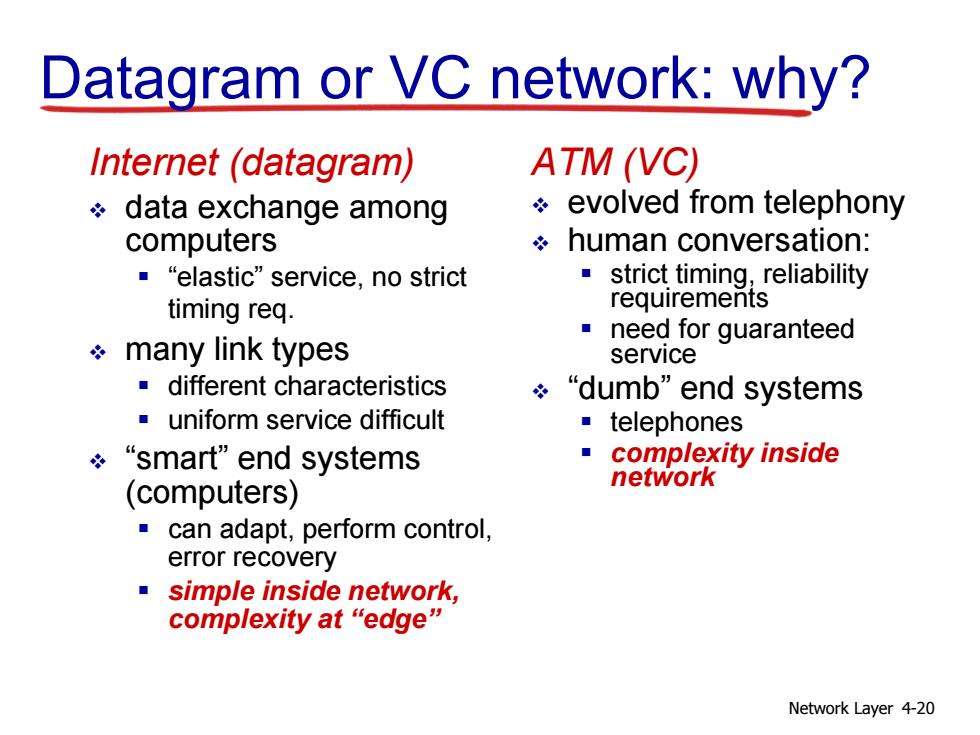
Datagram or VC network:why? Internet(datagram) ATM(VC) data exchange among evolved from telephony computers human conversation: ■“elastic”service,no strict strict timing,reliability timing req. requirements need for guaranteed many link types service different characteristics ÷“dumb”end systems uniform service difficult telephones “smart"end systems ■complexity inside network (computers) can adapt,perform control, error recovery simple inside network, complexity at“edge” Network Layer 4-20
Network Layer 4-20 Datagram or VC network: why? Internet (datagram) data exchange among computers “elastic” service, no strict timing req. many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult “smart” end systems (computers) can adapt, perform control, error recovery simple inside network, complexity at “edge” ATM (VC) evolved from telephony human conversation: strict timing, reliability requirements need for guaranteed service “dumb” end systems telephones complexity inside network