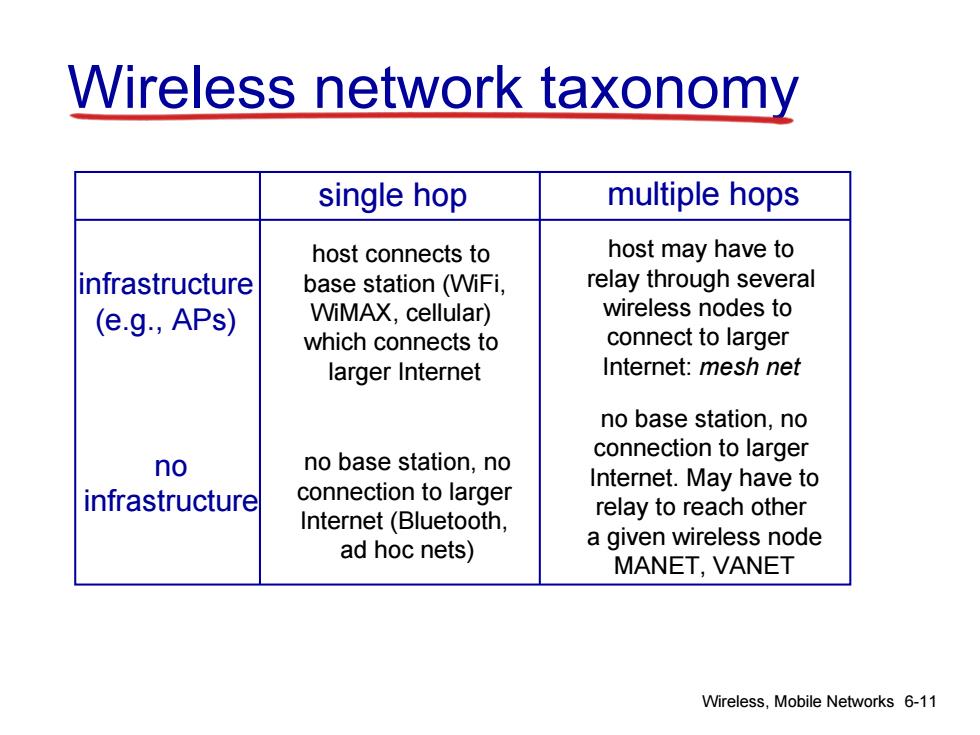
Wireless network taxonomy single hop multiple hops host connects to host may have to infrastructure base station(WiFi, relay through several (e.g.,APs) WiMAX,cellular) wireless nodes to which connects to connect to larger larger Internet Internet:mesh net no base station,no no no base station,no connection to larger Internet.May have to infrastructure connection to larger Internet(Bluetooth, relay to reach other ad hoc nets) a given wireless node MANET,VANET Wireless,Mobile Networks 6-11
Wireless, Mobile Networks 6-11 Wireless network taxonomy single hop multiple hops infrastructure (e.g., APs) no infrastructure host connects to base station (WiFi, WiMAX, cellular) which connects to larger Internet no base station, no connection to larger Internet (Bluetooth, ad hoc nets) host may have to relay through several wireless nodes to connect to larger Internet: mesh net no base station, no connection to larger Internet. May have to relay to reach other a given wireless node MANET, VANET
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Mobility Wireless 6.5 Principles:addressing 6.2 Wireless links, and routing to mobile users characteristics ·CDMA 6.6 Mobile IP 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless 6.7 Handling mobility in LANs ("Wi-Fi") cellular networks 6.4 Cellular Internet 6.8 Mobility and higher-layer Access protocols ■architecture standards (e.g.,GSM) 6.9 Summary Wireless,Mobile Networks 6-12
Wireless, Mobile Networks 6-12 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs (“Wi-Fi”) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5 Principles: addressing and routing to mobile users 6.6 Mobile IP 6.7 Handling mobility in cellular networks 6.8 Mobility and higher-layer protocols 6.9 Summary

Wireless Link Characteristics (1) important differences from wired link ... -decreased signal strength:radio signal attenuates as it propagates through matter(path loss) interference from other sources:standardized wireless network frequencies (e.g.,2.4 GHz) shared by other devices (e.g.,phone);devices (motors)interfere as well multipath propagation:radio signal reflects off objects ground,arriving ad destination at slightly different times ...make communication across (even a point to point) wireless link much more "difficult" Wireless,Mobile Networks 6-13
Wireless, Mobile Networks 6-13 Wireless Link Characteristics (1) important differences from wired link …. decreased signal strength: radio signal attenuates as it propagates through matter (path loss) interference from other sources: standardized wireless network frequencies (e.g., 2.4 GHz) shared by other devices (e.g., phone); devices (motors) interfere as well multipath propagation: radio signal reflects off objects ground, arriving ad destination at slightly different times …. make communication across (even a point to point) wireless link much more “difficult
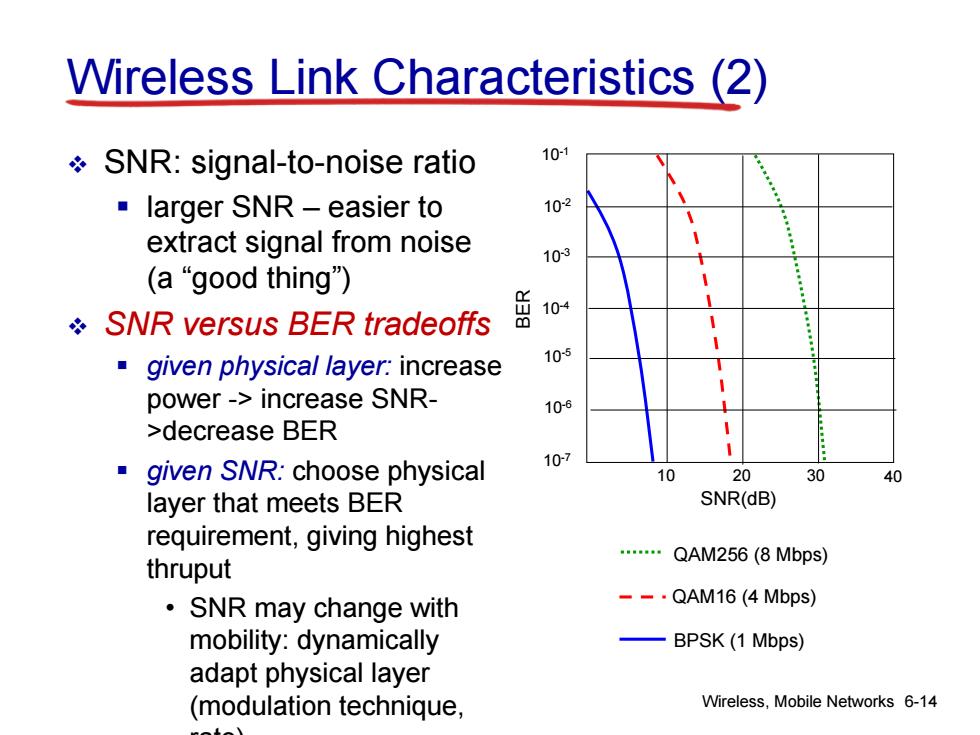
Wireless Link Characteristics (2) SNR:signal-to-noise ratio 101 larger SNR-easier to 10-2 extract signal from noise 103 (a“good thing") SNR versus BER tradeoffs given physical layer:increase 10 power->increase SNR- 10-6 >decrease BER given SNR:choose physical 10-7 20 layer that meets BER SNR(dB) requirement,giving highest ” QAM256(8 Mbps) thruput ·SNR may change with --·QAM16(4Mbps) mobility:dynamically BPSK(1 Mbps) adapt physical layer (modulation technique, Wireless,Mobile Networks 6-14
Wireless, Mobile Networks 6-14 Wireless Link Characteristics (2) SNR: signal-to-noise ratio larger SNR – easier to extract signal from noise (a “good thing”) SNR versus BER tradeoffs given physical layer: increase power -> increase SNR- >decrease BER given SNR: choose physical layer that meets BER requirement, giving highest thruput • SNR may change with mobility: dynamically adapt physical layer (modulation technique, rate) 10 20 30 40 QAM256 (8 Mbps) QAM16 (4 Mbps) BPSK (1 Mbps) SNR(dB) BER 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-5 10-6 10-7 10-4
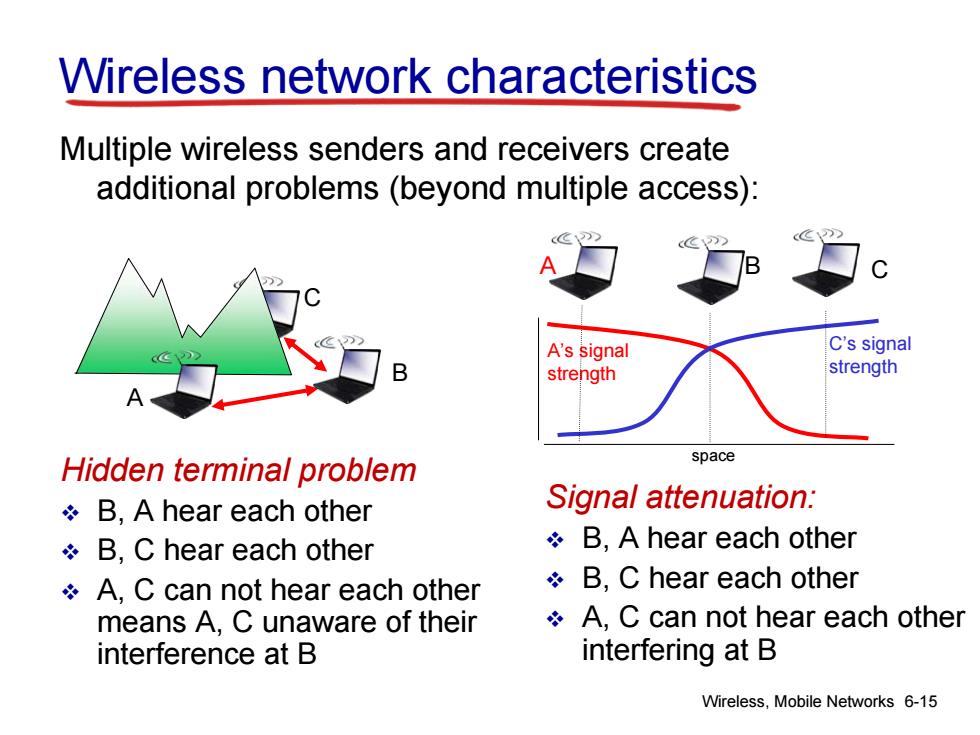
Wireless network characteristics Multiple wireless senders and receivers create additional problems(beyond multiple access): A's signal C's signal strength strength Hidden terminal problem space B,A hear each other Signal attenuation: B,C hear each other B,A hear each other A,C can not hear each other B,C hear each other means A,C unaware of their A,C can not hear each other interference at B interfering at B Wireless,Mobile Networks 6-15
Wireless, Mobile Networks 6-15 Wireless network characteristics Multiple wireless senders and receivers create additional problems (beyond multiple access): A B C Hidden terminal problem B, A hear each other B, C hear each other A, C can not hear each other means A, C unaware of their interference at B A B C A’s signal strength space C’s signal strength Signal attenuation: B, A hear each other B, C hear each other A, C can not hear each other interfering at B