Addressing processes to receive messages, identifier includes both IP process must have address and port numbers identifier associated with process host device has unique on host. 32-bit IP address example port numbers: Q:does IP address of ■HTTP server:80 host on which process ■mail server:25 runs suffice for identifying to send HTTP message to the procesaany gaia.cs.umass.edu web processes can be server: running on same host ■IP address:128.119.245.12 port number:80 ÷more shortly.. Application Layer 2-11
Application Layer 2-11 Addressing processes to receive messages, process must have identifier host device has unique 32-bit IP address Q: does IP address of host on which process runs suffice for identifying the process? identifier includes both IP address and port numbers associated with process on host. example port numbers: HTTP server: 80 mail server: 25 to send HTTP message to gaia.cs.umass.edu web server: IP address: 128.119.245.12 port number: 80 more shortly… A: no, many processes can be running on same host
App-layer protocol defines types of messages open protocols: exchanged, defined in RFCs e.g.,request, allows for response interoperability message syntax: e.g.,HTTP,SMTP what fields in proprietary protocols: messages how fields are delineated ÷e.g,Skype message semantics meaning of information in fields rules for when and how processes send respond to messages Application Layer 2-12
Application Layer 2-12 App-layer protocol defines types of messages exchanged, e.g., request, response message syntax: what fields in messages & how fields are delineated message semantics meaning of information in fields rules for when and how processes send & respond to messages open protocols: defined in RFCs allows for interoperability e.g., HTTP, SMTP proprietary protocols: e.g., Skype
What transport service does an app need? data integrity throughput some apps (e.g.,file ÷some apps(e.g., transfer,web transactions) multimedia)require require 100%reliable data minimum amount of transfer throughput to be other apps (e.g.,audio)can “effective” tolerate some loss other apps ("elastic timing apps)make use of whatever throughput some apps (e.g., they get Internet telephony, security interactive games) require low delay to be encryption,data integrity, “effective'” Application Layer 2-13
Application Layer 2-13 What transport service does an app need? data integrity some apps (e.g., file transfer, web transactions) require 100% reliable data transfer other apps (e.g., audio) can tolerate some loss timing some apps (e.g., Internet telephony, interactive games) require low delay to be “effective” throughput some apps (e.g., multimedia) require minimum amount of throughput to be “effective” other apps (“elastic apps”) make use of whatever throughput they get security encryption, data integrity, …
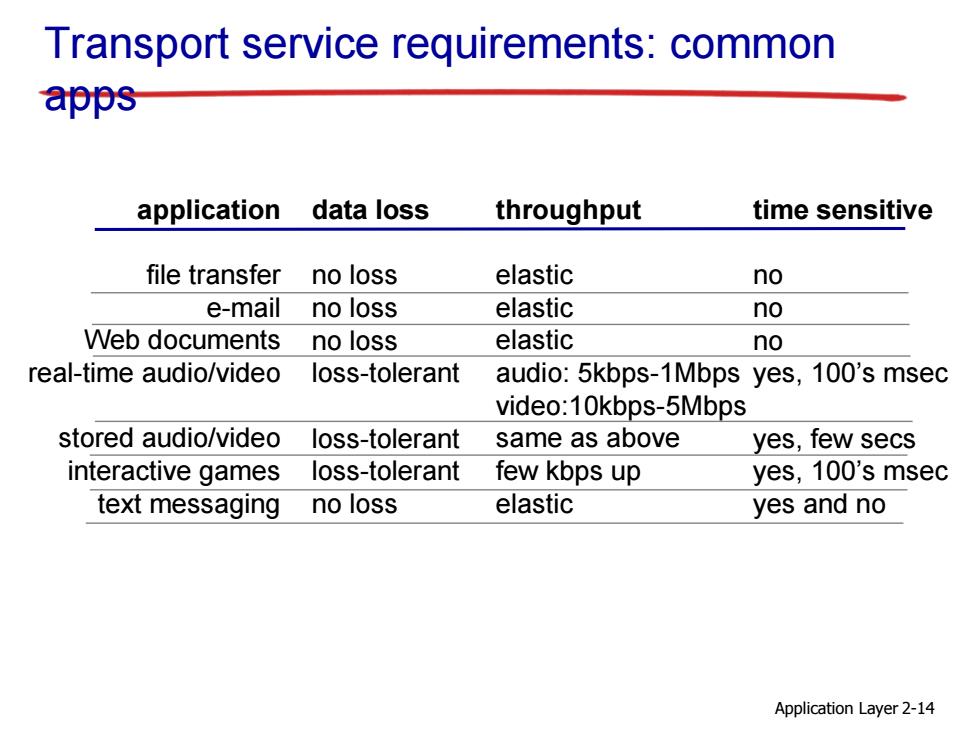
Transport service requirements:common apps application data loss throughput time sensitive file transfer no loss elastic no e-mail no loss elastic no Web documents no loss elastic no real-time audio/video loss-tolerant audio:5kbps-1Mbps yes,100's msec video:10kbps-5Mbps stored audio/video loss-tolerant same as above yes,few secs interactive games loss-tolerant few kbps up yes,100's msec text messaging no loss elastic yes and no Application Layer 2-14
Application Layer 2-14 Transport service requirements: common apps application file transfer e-mail Web documents real-time audio/video stored audio/video interactive games text messaging data loss no loss no loss no loss loss-tolerant loss-tolerant loss-tolerant no loss throughput elastic elastic elastic audio: 5kbps-1Mbps video:10kbps-5Mbps same as above few kbps up elastic time sensitive no no no yes, 100’s msec yes, few secs yes, 100’s msec yes and no
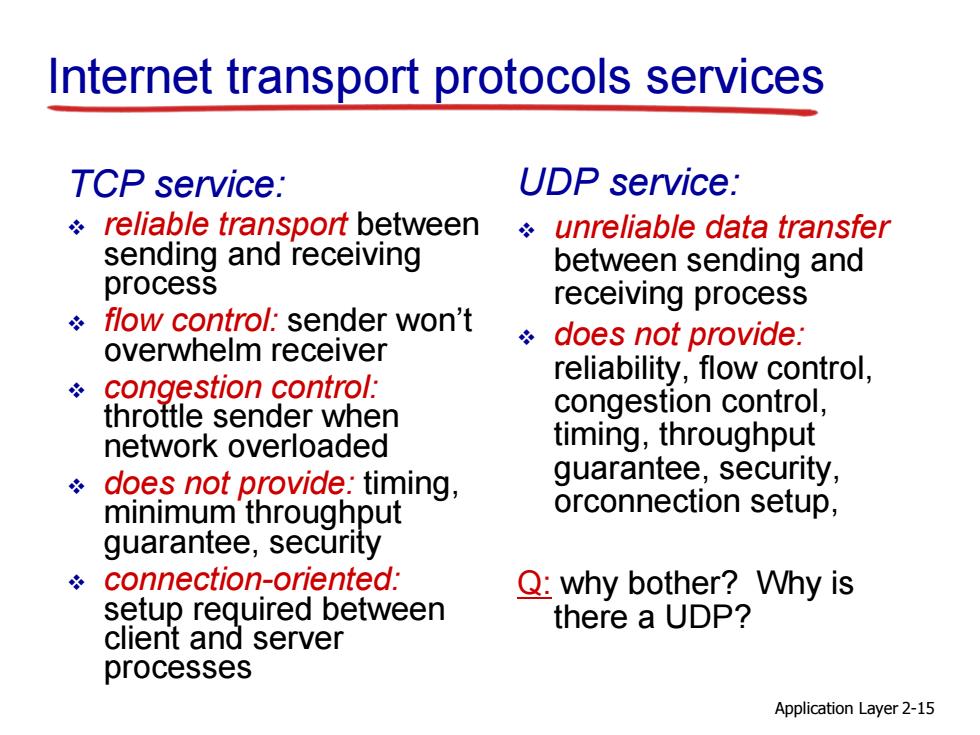
Internet transport protocols services TCP service: UDP service: reliable transport betweenunreliable data transfer sending and receiving between sending and process receiving process flow control:sender won't overwhelm receiver does not provide: *congestion control: reliability,flow control, throttle sender when congestion control, network overloaded timing,throughput does not provide:timing, guarantee,security, minimum throughput orconnection setup, guarantee,security connection-oriented: Q:why bother?Why is setup required between there a UDP? client and server processes Application Layer 2-15
Application Layer 2-15 Internet transport protocols services TCP service: reliable transport between sending and receiving process flow control: sender won’t overwhelm receiver congestion control: throttle sender when network overloaded does not provide: timing, minimum throughput guarantee, security connection-oriented: setup required between client and server processes UDP service: unreliable data transfer between sending and receiving process does not provide: reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, throughput guarantee, security, orconnection setup, Q: why bother? Why is there a UDP?