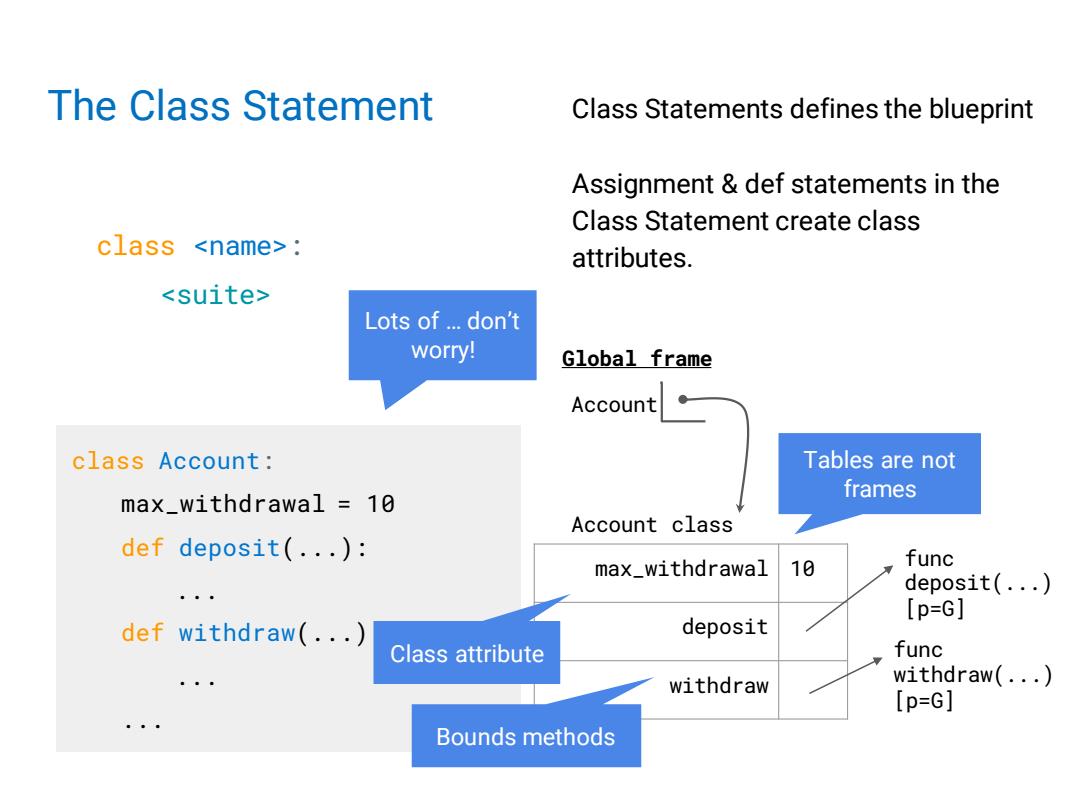
The Class Statement Class Statements defines the blueprint Assignment def statements in the Class Statement create class class <name>: attributes. <suite> Lots of...don't worry! Global frame Account class Account: Tables are not frames max_withdrawal 10 Account class def deposit(...): max_withdrawal 10 func deposit(...) 年 [p=G] def withdraw(.·.) deposit Class attribute func withdraw withdraw(...) [p=G] Bounds methods
The Class Statement class Account: max_withdrawal = 10 def deposit(...): ... def withdraw(...): ... ... class <name>: <suite> Class Statements defines the blueprint Assignment & def statements in the Class Statement create class attributes. Global frame Account Account class func withdraw(...) [p=G] func deposit(...) [p=G] Tables are not frames Lots of … don’t worry! max_withdrawal 10 deposit withdraw Class attribute Bounds methods

The Class Statement Before we start implementing our methods,we need to talk about how to create Accounts. Idea:All bank accounts have a balance and an account holder.These are not shared across Accounts. When a class is called: 1.A new instance of that class is created. 2.The__init_method of a class is called with the new object as its first argument(named self),along with additional arguments provided in the call expression. _init_is called class Account: the constructor ··。 def __init__(self,account_holder): self.balance 0 self.holder account_holder
The Class Statement Before we start implementing our methods, we need to talk about how to create Accounts. Idea: All bank accounts have a balance and an account holder. These are not shared across Accounts. When a class is called: 1. A new instance of that class is created. 2. The __init__ method of a class is called with the new object as its first argument (named self), along with additional arguments provided in the call expression. class Account: ... def __init__(self, account_holder): self.balance = 0 self.holder = account_holder ... __init__ is called the constructor