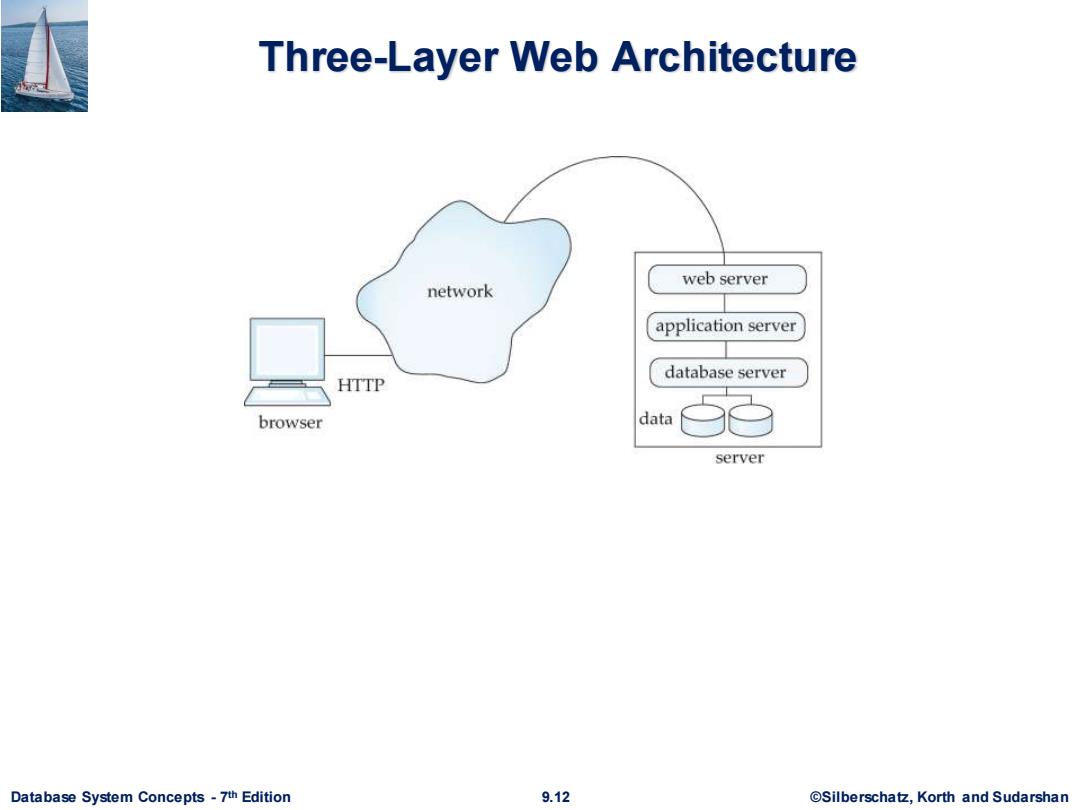
Three-Layer Web Architecture web server network application server database server HTTP browser data server Database System Concepts-7th Edition 9.12 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 9.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Three-Layer Web Architecture
HTTP and Sessions The HTTP protocol is connectionless That is,once the server replies to a request,the server closes the connection with the client,and forgets all about the request In contrast,Unix logins,and JDBC/ODBC connections stay connected until the client disconnects retaining user authentication and other information Motivation:reduces load on server operating systems have tight limits on number of open connections on a machine Information services need session information E.g.,user authentication should be done only once per session Solution:use a cookie Database System Concepts-7th Edition 9.14 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 9.14 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition HTTP and Sessions ▪ The HTTP protocol is connectionless • That is, once the server replies to a request, the server closes the connection with the client, and forgets all about the request • In contrast, Unix logins, and JDBC/ODBC connections stay connected until the client disconnects ▪ retaining user authentication and other information • Motivation: reduces load on server ▪ operating systems have tight limits on number of open connections on a machine ▪ Information services need session information • E.g., user authentication should be done only once per session ▪ Solution: use a cookie

Sessions and Cookies A cookie is a small piece of text containing identifying information Sent by server to browser Sent on first interaction,to identify session Sent by browser to the server that created the cookie on further interactions part of the HTTP protocol Server saves information about cookies it issued,and can use it when serving a request .E.g.,authentication information,and user preferences Cookies can be stored permanently or for a limited time Database System Concepts-7th Edition 9.15 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 9.15 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Sessions and Cookies ▪ A cookie is a small piece of text containing identifying information • Sent by server to browser ▪ Sent on first interaction, to identify session • Sent by browser to the server that created the cookie on further interactions ▪ part of the HTTP protocol • Server saves information about cookies it issued, and can use it when serving a request ▪ E.g., authentication information, and user preferences ▪ Cookies can be stored permanently or for a limited time
Servlets Java Servlet specification defines an APl for communication between the Web/application server and application program running in the server E.g.,methods to get parameter values from Web forms,and to send HTML text back to client Application program(also called a servlet)is loaded into the server Each request spawns a new thread in the server thread is closed once the request is serviced Programmer creates a class that inherits from HttpServlet And overrides methods doGet,doPost,... Mapping from servlet name (accessible via HTTP),to the servlet class is done in a file web.xml Done automatically by most IDEs when you create a Servlet using the IDE Database System Concepts-7th Edition 9.16 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 9.16 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Servlets ▪ Java Servlet specification defines an API for communication between the Web/application server and application program running in the server • E.g., methods to get parameter values from Web forms, and to send HTML text back to client ▪ Application program (also called a servlet) is loaded into the server • Each request spawns a new thread in the server ▪ thread is closed once the request is serviced • Programmer creates a class that inherits from HttpServlet ▪ And overrides methods doGet, doPost, … • Mapping from servlet name (accessible via HTTP), to the servlet class is done in a file web.xml ▪ Done automatically by most IDEs when you create a Servlet using the IDE

Example Servlet Code import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; public class PersonQueryServlet extends HttpServlet public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException,IOException response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out response.getWriter(); out.printIn("<HEAD><TITLE>Query Result</TITLE></HEAD>"); out.printin("<BODY>"); ....BODY OF SERVLET (next slide)... out.printIn("</BODY>"); out.close(); } } Database System Concepts-7th Edition 9.17 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 9.17 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Example Servlet Code import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; public class PersonQueryServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<HEAD><TITLE> Query Result</TITLE></HEAD>"); out.println("<BODY>"); ….. BODY OF SERVLET (next slide) … out.println("</BODY>"); out.close(); } }