
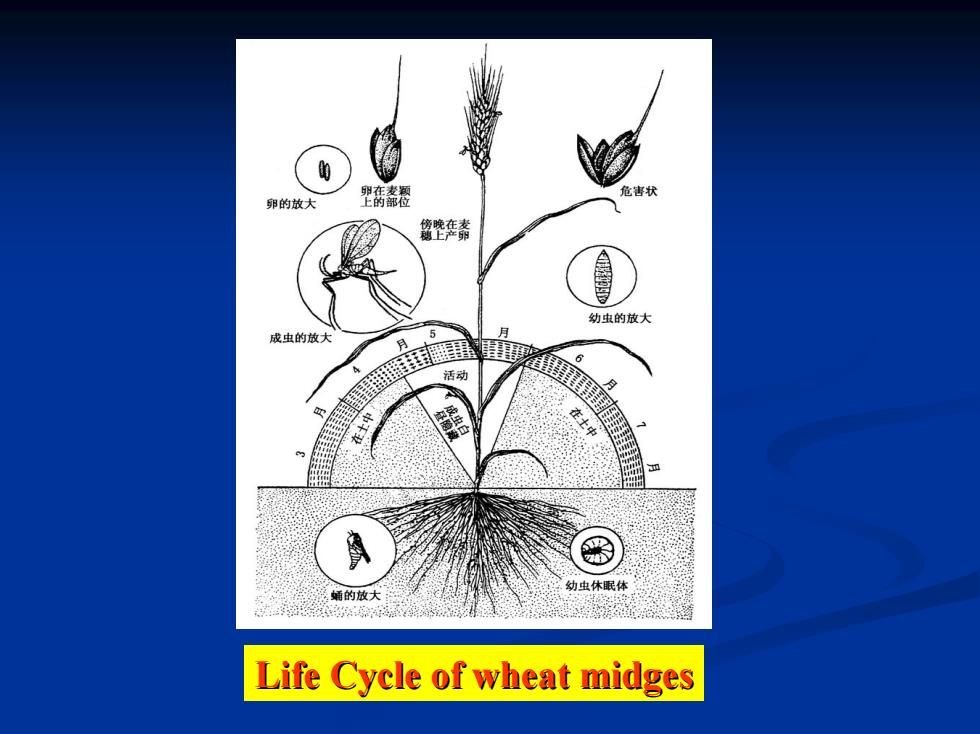
3.Life Cycle ▣1 generation/year; Overwinter and oversummer as grown larvae with round cocoon in soil; Diapause larvae can prolong diapause for a long time.Longest prolonged time is more than 7 years,even 12 years to Sitodiplosis mosellana or less than 4-5 years to Contarinia tritici
1 generation/year; Overwinter and oversummer as grown larvae with round cocoon in soil; Diapause larvae can prolong diapause for a long time. Longest prolonged time is more than 7 years, even 12 years to Sitodiplosis mosellana or less than 4-5 years to Contarinia tritici. 3. Life Cycle 3. Life Cycle
卵的放大 型斋蒂 幼虫的放大 成虫的放大 套宣人 活动 在土中 幼虫休眠 蛹的放大 Life Cycle of wheat midges
Life Cycle of wheat midges Life Cycle of wheat midges

3.Life Cycle A close relationship occurs between the stages of the wheat midge and development of wheat found in valley areas of Yellew River and Huai River: Overwintered larvae come out from cocoon to surface of soil during shooting stage of wheat; Larvae pupate when wheat enters booting stage;
A close relationship occurs between the stages of the wheat midge and development of wheat found in valley areas of Yellew River and Huai River: Overwintered larvae come out from cocoon to surface of soil during shooting stage of wheat; Larvae pupate when wheat enters booting stage; 3. Life Cycle 3. Life Cycle

3.Life Cycle Adults largely emerge and oviposit during heading stage. Peak of egg hatching is concurrent with blossoming and grouting stage of wheat; Larvae become grown and leave wheat heads to drop into soil to oversummer and overwinter with round cocoons when wheat become mature
Adults largely emerge and oviposit during heading stage. Peak of egg hatching is concurrent with blossoming and grouting stage of wheat; Larvae become grown and leave wheat heads to drop into soil to oversummer and overwinter with round cocoons when wheat become mature. 3. Life Cycle 3. Life Cycle

4.Behaviors Adults fear strong light and high temp, so most frequent activity in early morning and nightfall; Eggs lay on wheat heads individually; adults prefer to choose heads without blossoms to oviposit;very few eggs found on blossomed heads; Newly hatched larvae intrude from gap between inner glume and outer glume to suck sap of grouting kernels
Adults fear strong light and high temp, so most frequent activity in early morning and nightfall; Eggs lay on wheat heads individually; adults prefer to choose heads without blossoms to oviposit; very few eggs found on blossomed heads; Newly hatched larvae intrude from gap between inner glume and outer glume to suck sap of grouting kernels 4. Behaviors 4. Behaviors