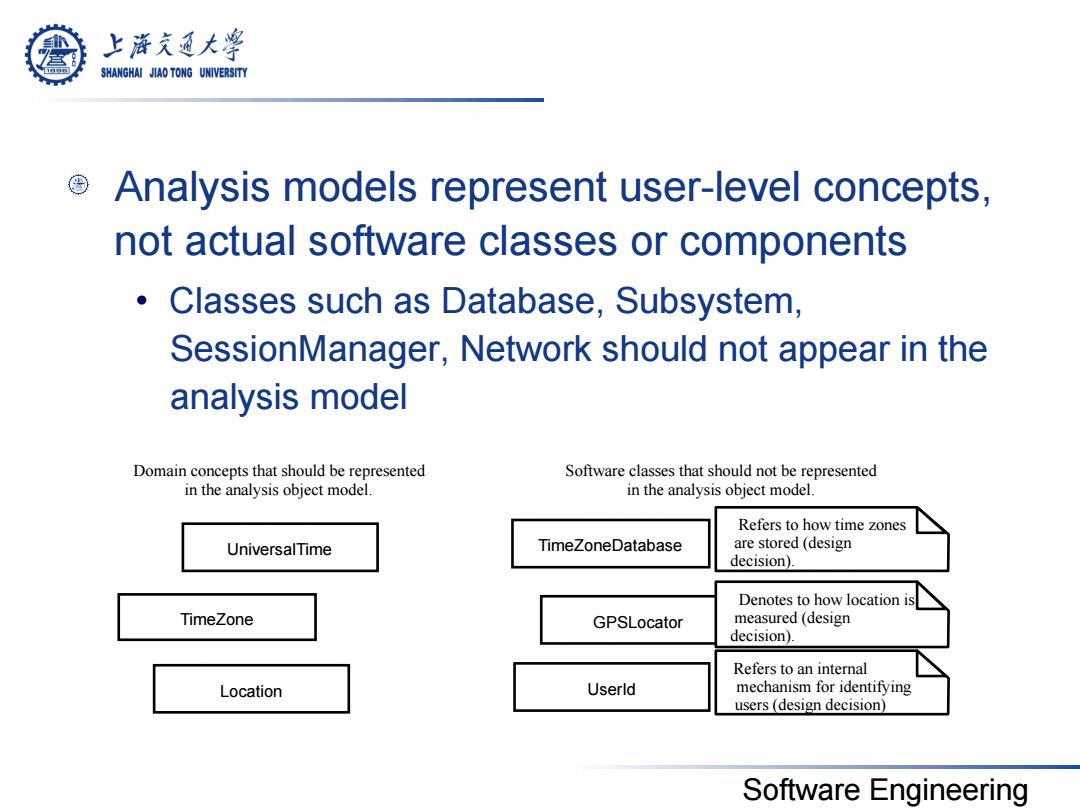
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Analysis models represent user-level concepts, not actual software classes or components Classes such as Database,Subsystem, SessionManager,Network should not appear in the analysis model Domain concepts that should be represented Software classes that should not be represented in the analysis object model. in the analysis object model. Refers to how time zones UniversalTime TimeZoneDatabase are stored(design decision). Denotes to how location is TimeZone GPSLocator measured(design decision). Refers to an internal Location Userld mechanism for identifying users(design decision) Software Engineering
Software Engineering Analysis models represent user-level concepts, not actual software classes or components • Classes such as Database, Subsystem, SessionManager, Network should not appear in the analysis model UniversalTime TimeZone Location TimeZoneDatabase GPSLocator UserId Software classes that should not be represented in the analysis object model. Domain concepts that should be represented in the analysis object model. Refers to how time zones are stored (design decision). Denotes to how location is measured (design decision). Refers to an internal mechanism for identifying users (design decision)

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.Analysis Activities Software Engineering
Software Engineering 3. Analysis Activities

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Analysis Activities Main goal:Find the important abstractions Steps during object modeling 1.Object identification Identifying Entity Objects Identifying Boundary Object Identifying Control Objects 2.Mapping Use Cases to Objects with Sequence Diagrams 3.Modeling Interactions among Objects with CRC Cards 4.Identifying Associations,Aggregates and Attributes 5.Modeling State-Dependent Behavior of Individual Objects 6.Modeling Inheritance Relationships 7.Reviewing Order of steps Goal:get the desired abstractions Order of steps secondary,only a heuristic Iteration is important Software Engineering
Software Engineering Analysis Activities Main goal: Find the important abstractions Steps during object modeling 1. Object identification Identifying Entity Objects Identifying Boundary Object Identifying Control Objects 2. Mapping Use Cases to Objects with Sequence Diagrams 3. Modeling Interactions among Objects with CRC Cards 4. Identifying Associations, Aggregates and Attributes 5. Modeling State-Dependent Behavior of Individual Objects 6. Modeling Inheritance Relationships 7. Reviewing Order of steps • Goal: get the desired abstractions • Order of steps secondary, only a heuristic • Iteration is important

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.1 Object Identifications Software Engineering
Software Engineering 3.1 Object Identifications

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.1.1 Object Identification © Identify the boundaries of the system Ildentify the important entities in the system © Object identification is crucial to object-oriented modeling Basic assumption: 1.We can find the objects for a new software system (Forward Engineering) 2.We can identify the objects in an existing system (Reverse Engineering) Software Engineering
Software Engineering 3.1.1 Object Identification Identify the boundaries of the system Identify the important entities in the system Object identification is crucial to object-oriented modeling Basic assumption: 1. We can find the objects for a new software system (Forward Engineering) 2. We can identify the objects in an existing system (Reverse Engineering)