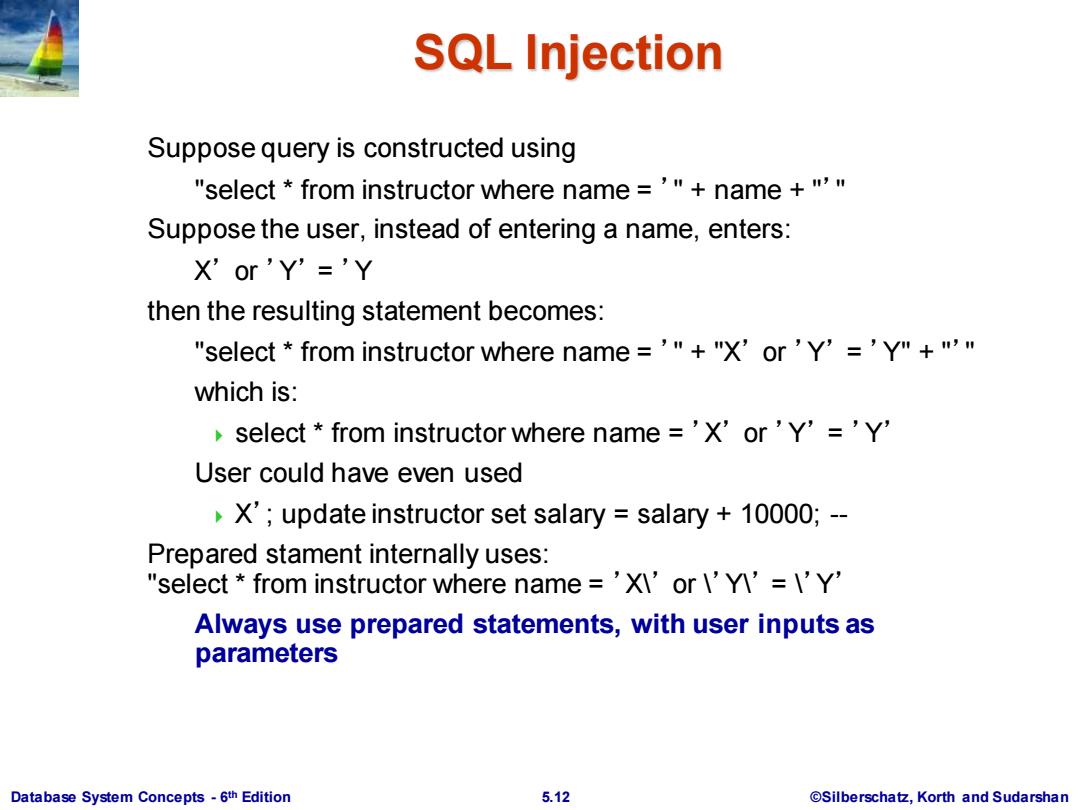
SQL Injection Suppose query is constructed using "select from instructor where name ='"name +"' Suppose the user,instead of entering a name,enters: X'or'Y'='Y then the resulting statement becomes: "select from instructor where name='"+"X'or 'Y'=YI +"' which is: select from instructor where name ='X'or 'Y'='Y' User could have even used X';update instructor set salary salary 10000;-- Prepared stament internally uses: "select from instructor where name ='X\'or ''=I'Y' Always use prepared statements,with user inputs as parameters Database System Concepts-6th Edition 5.12 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 5.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition SQL Injection Suppose query is constructed using "select * from instructor where name = ’" + name + "’" Suppose the user, instead of entering a name, enters: X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y then the resulting statement becomes: "select * from instructor where name = ’" + "X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y" + "’" which is: select * from instructor where name = ’X’ or ’Y’ = ’Y’ User could have even used X’; update instructor set salary = salary + 10000; -- Prepared stament internally uses: "select * from instructor where name = ’X\’ or \’Y\’ = \’Y’ Always use prepared statements, with user inputs as parameters
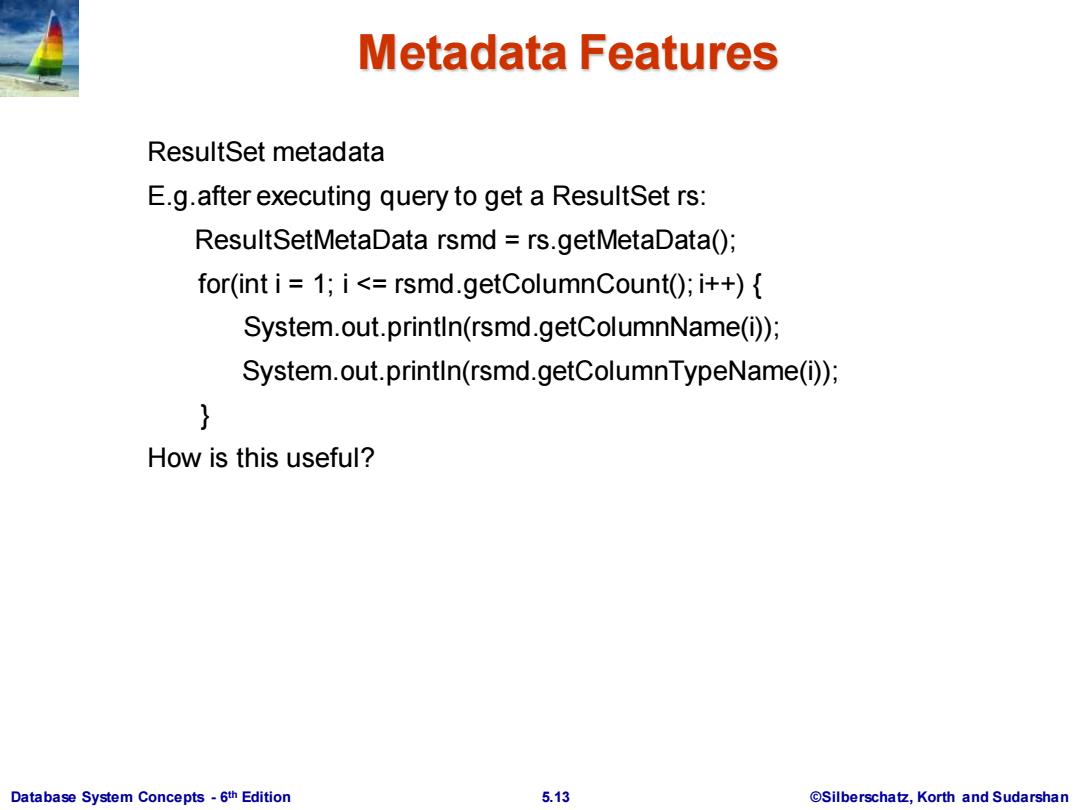
Metadata Features ResultSet metadata E.g.after executing query to get a ResultSet rs: ResultSetMetaData rsmd rs.getMetaData(); for(int i 1;i<=rsmd.getColumnCount(;i++){ System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnName(i)); System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnTypeName(i)); How is this useful? Database System Concepts-6th Edition 5.13 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 5.13 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Metadata Features ResultSet metadata E.g.after executing query to get a ResultSet rs: ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); for(int i = 1; i <= rsmd.getColumnCount(); i++) { System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnName(i)); System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnTypeName(i)); } How is this useful?
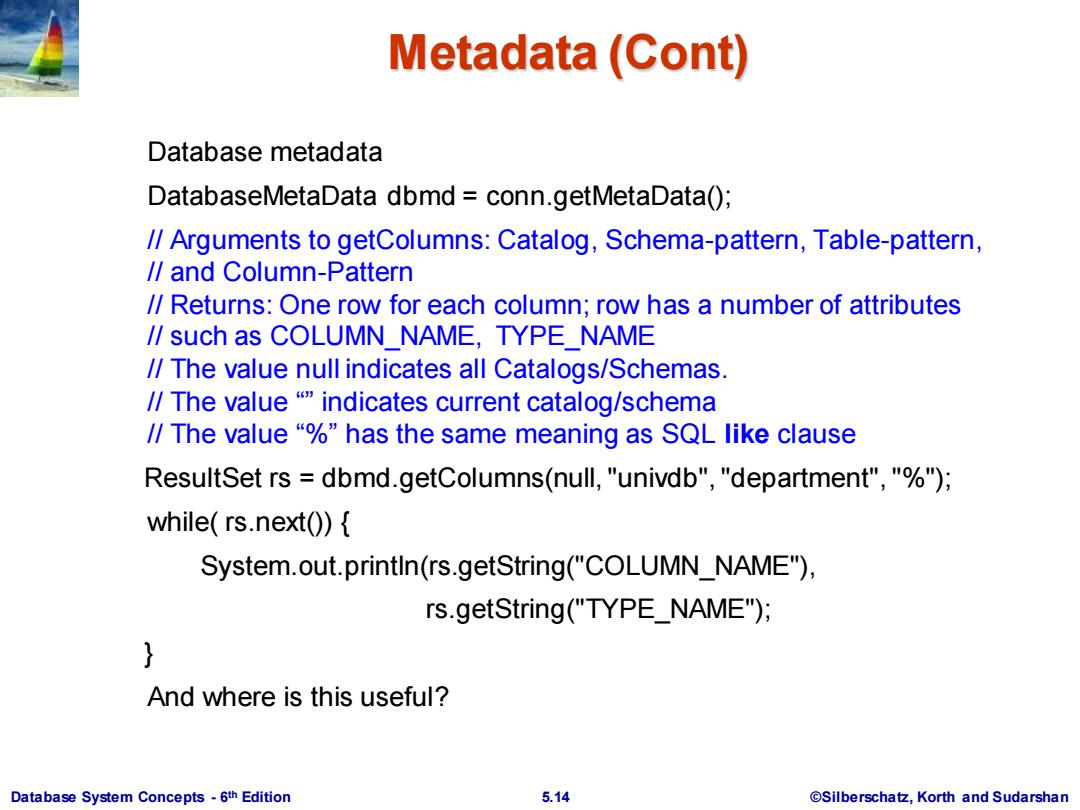
Metadata(Cont) Database metadata DatabaseMetaData dbmd conn.getMetaData(); /Arguments to getColumns:Catalog,Schema-pattern,Table-pattern, /and Column-Pattern /Returns:One row for each column;row has a number of attributes /such as COLUMN NAME,TYPE NAME /The value null indicates all Catalogs/Schemas. /The value "P indicates current catalog/schema /The value"%"has the same meaning as SQL like clause ResultSet rs dbmd.getColumns(null,"univdb","department","%") while(rs.next(){ System.out.println(rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"), rs.getString("TYPE_NAME"); And where is this useful? Database System Concepts-6th Edition 5.14 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 5.14 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Metadata (Cont) Database metadata DatabaseMetaData dbmd = conn.getMetaData(); // Arguments to getColumns: Catalog, Schema-pattern, Table-pattern, // and Column-Pattern // Returns: One row for each column; row has a number of attributes // such as COLUMN_NAME, TYPE_NAME // The value null indicates all Catalogs/Schemas. // The value “” indicates current catalog/schema // The value “%” has the same meaning as SQL like clause ResultSet rs = dbmd.getColumns(null, "univdb", "department", "%"); while( rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"), rs.getString("TYPE_NAME"); } And where is this useful?
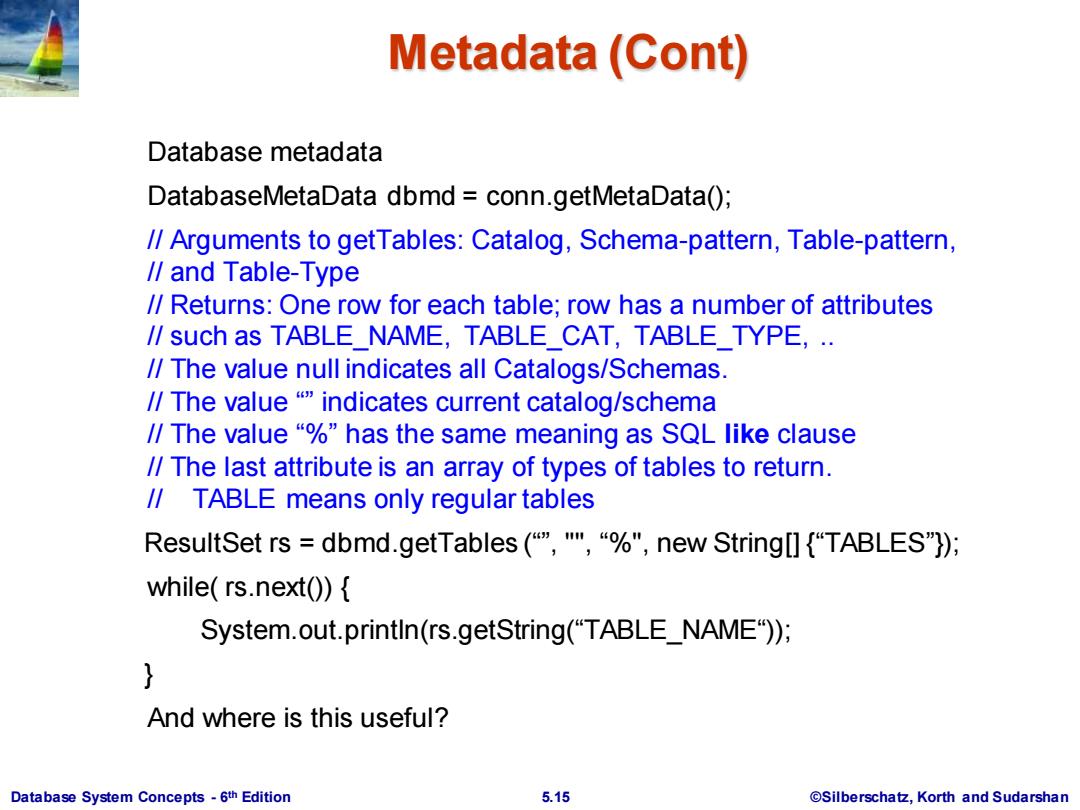
Metadata(Cont) Database metadata DatabaseMetaData dbmd conn.getMetaData(); /Arguments to getTables:Catalog,Schema-pattern,Table-pattern, /and Table-Type /Returns:One row for each table;row has a number of attributes /such as TABLE NAME,TABLE CAT,TABLE TYPE,.. /The value null indicates all Catalogs/Schemas. /The value indicates current catalog/schema /The value"%has the same meaning as SQL like clause /The last attribute is an array of types of tables to return. /TABLE means only regular tables ResultSet rs=dbmd.getTables(“",",“%",new String[]{“TABLES"): while(rs.next(){ System.out.println(rs.getString("TABLE_NAME")); } And where is this useful? Database System Concepts-6th Edition 5.15 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 5.15 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Metadata (Cont) Database metadata DatabaseMetaData dbmd = conn.getMetaData(); // Arguments to getTables: Catalog, Schema-pattern, Table-pattern, // and Table-Type // Returns: One row for each table; row has a number of attributes // such as TABLE_NAME, TABLE_CAT, TABLE_TYPE, .. // The value null indicates all Catalogs/Schemas. // The value “” indicates current catalog/schema // The value “%” has the same meaning as SQL like clause // The last attribute is an array of types of tables to return. // TABLE means only regular tables ResultSet rs = dbmd.getTables (“”, "", “%", new String[] {“TABLES”}); while( rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString(“TABLE_NAME“)); } And where is this useful?
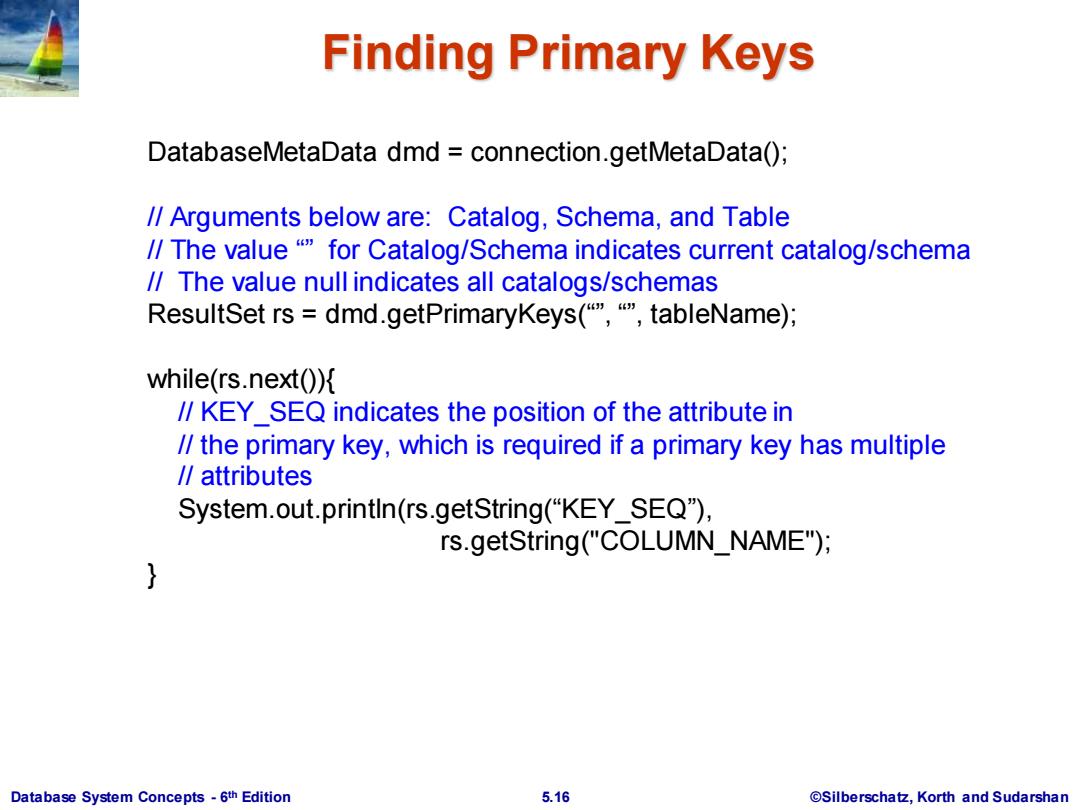
Finding Primary Keys DatabaseMetaData dmd connection.getMetaData(); /Arguments below are:Catalog,Schema,and Table /The value"P for Catalog/Schema indicates current catalog/schema /The value null indicates all catalogs/schemas ResultSet rs dmd.getPrimaryKeys(,tableName); while(rs.next()){ /KEY SEQ indicates the position of the attribute in /the primary key,which is required if a primary key has multiple /attributes System.out.printin(rs.getString("KEY_SEQ), rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"); } Database System Concepts-6th Edition 5.16 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 5.16 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Finding Primary Keys DatabaseMetaData dmd = connection.getMetaData(); // Arguments below are: Catalog, Schema, and Table // The value “” for Catalog/Schema indicates current catalog/schema // The value null indicates all catalogs/schemas ResultSet rs = dmd.getPrimaryKeys(“”, “”, tableName); while(rs.next()){ // KEY_SEQ indicates the position of the attribute in // the primary key, which is required if a primary key has multiple // attributes System.out.println(rs.getString(“KEY_SEQ”), rs.getString("COLUMN_NAME"); }