
Sum Digits 1 def sum_digits(n): 2 """Calculates the sum of the digits n 3 >>sum_digits(8) 4 8 5 >>sum_digits(18) 6 9 7 >>sum_digits(2018) 8 11 9 111111 10 if n 10: 11 return n 12 else: 13 all_but_last,last n /10,n 10 14 return sum_digits(all_but_last)+last
Sum Digits 1 def sum_digits(n): 2 """Calculates the sum of the digits n 3 >>> sum_digits(8) 4 8 5 >>> sum_digits(18) 6 9 7 >>> sum_digits(2018) 8 11 9 """ 10 if n < 10: 11 return n 12 else: 13 all_but_last, last = n // 10, n % 10 14 return sum_digits(all_but_last) + last

Order of Recursive Calls
Order of Recursive Calls
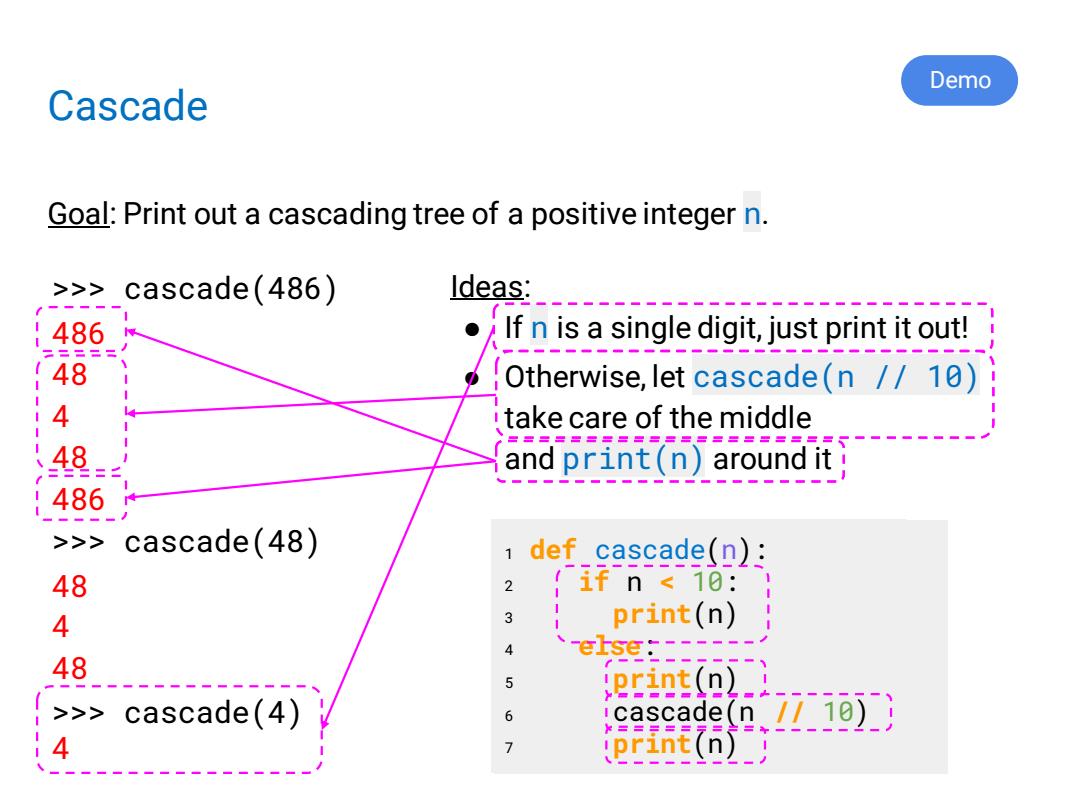
Demo Cascade Goal:Print out a cascading tree of a positive integer n. >>> cascade(486) ldeas: :486 If n is a single digit,just print it out! ==== 48 Otherwise,let cascade(n /10) 4 take care of the middle ===================== 48 and print(n)around it! 486 >>> cascade(48) 1 def cascade(n): 48 2 if n<18:1 4 3 print(n) 4 48 'print(n) >>cascade(4) 6 icascade(n 77 10)) ==号=== 4 7 iprint(n)_
1 def cascade cascade(n): 2 if n < 10: 3 print(n) 1 def cascade(n): 2 if n < 10: 3 print(n) 4 else: 5 print(n) 6 cascade(n // 10) 7 print(n) Cascade Goal: Print out a cascading tree of a positive integer n. >>> cascade(486) 486 48 4 48 486 >>> cascade(48) 48 4 48 >>> cascade(4) 4 Ideas: ● If n is a single digit, just print it out! ● Otherwise, let cascade(n // 10) take care of the middle and print(n) around it Demo
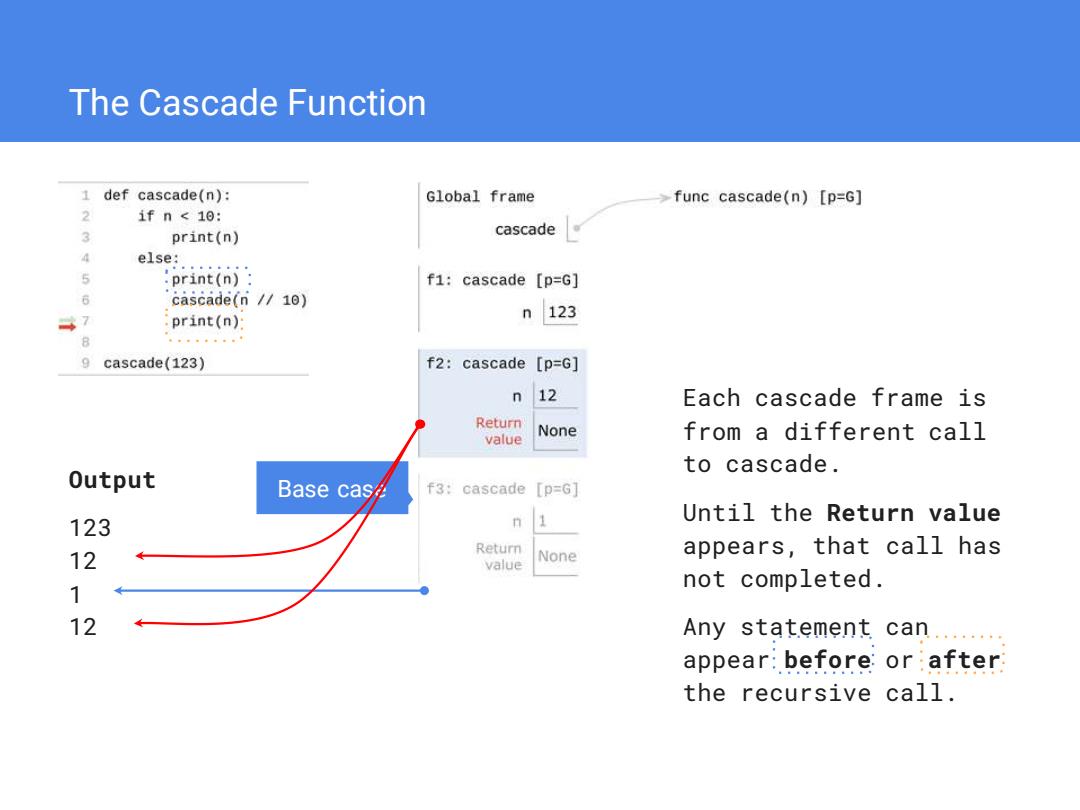
The Cascade Function 1 def cascade(n): Global frame func cascade(n)[p=G] 1fn<10: 2 print(n) cascade 4 else: 5 :print(n): f1:cascade [p=G] 6 cascade(n//10) 47 print(n) n123 8 。中。。t。。。 9 cascade(123) f2:cascade [p=G] 12 Each cascade frame is Return value None from a different call to cascade. Output Base cas∥ f3:cascade【p=G] 123 n 1 Until the Return value Return 12 value None appears,that call has 1 not completed. 12 Any statement can...... appear:before:or after the recursive call
The Cascade Function Each cascade frame is from a different call to cascade. Until the Return value appears, that call has not completed. Any statement can appear before or after the recursive call. Output 123 12 1 12 Base case
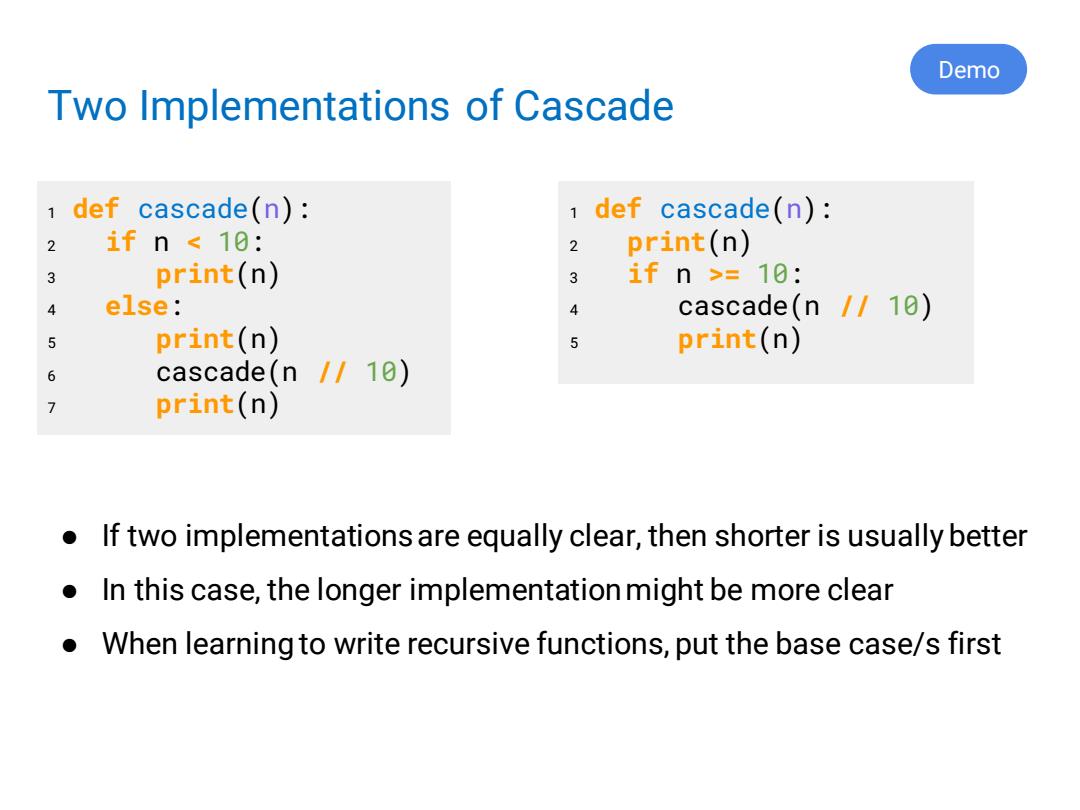
Demo Two Implementations of Cascade 1 def cascade(n): 1 def cascade(n): 2 if n 10: 2 print(n) 3 print(n) 3 ifn>=-10: 4 else: 4 cascade(n /10) 5 print(n) 5 print(n) 6 cascade(n /10) 7 print(n) If two implementations are equally clear,then shorter is usually better ● In this case,the longer implementation might be more clear When learning to write recursive functions,put the base case/s first
Two Implementations of Cascade ● If two implementations are equally clear, then shorter is usually better ● In this case, the longer implementation might be more clear ● When learning to write recursive functions, put the base case/s first 1 def cascade(n): 2 if n < 10: 3 print(n) 4 else: 5 print(n) 6 cascade(n // 10) 7 print(n) 1 def cascade(n): 2 print(n) 3 if n >= 10: 4 cascade(n // 10) 5 print(n) Demo