
1907 15-11 C、 C=a+bY E S=-a+(1-b)Y a 450 0 -a Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-11 c、s Y O C=a+bY a Y0 E 450 S=-a+(1-b)Y -a
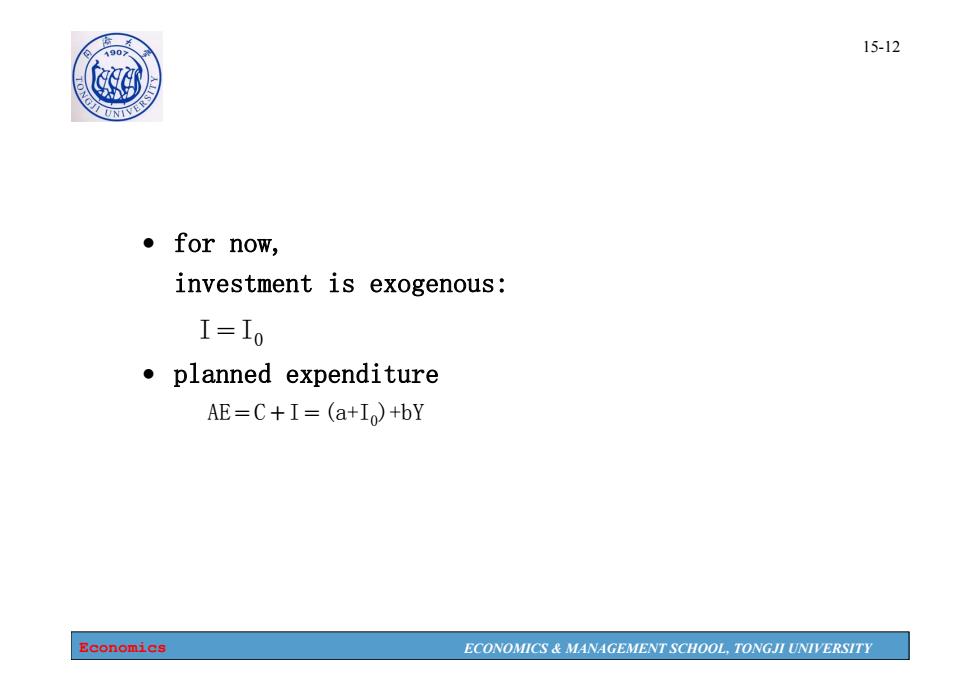
A90 15-12 欧 ●for now, investment is exogenous: I=Io 。planned expenditure AE=C+I=(a+Io)+bY Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-12 • for now, investment is exogenous: I=I0 • planned expenditure AE=C+I=(a+I0)+bY

1907 15-13 12.1.2 Determination of Equilibrium Income and Output 1,Equilibrium condition: Actual expenditure=Planned expenditure Y=AE Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-13 • 1,Equilibrium condition: Actual expenditure=Planned expenditure Y=AE 12.1.2 Determination of Equilibrium Income and Output

490 15-14 AE AE-45° planned AE=Y expenditure 45° income,output,Y Aggregate expenditures will be equal to total output for all points along the 45line from the origin. The 45 line maps out potential equilibrium levels of output for the Keynesian model. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-14 AE-45º income, output, Y AE planned expenditure 45º AE=Y • Aggregate expenditures will be equal to total output for all points along the 45° line from the origin. • The 45° line maps out potential equilibrium levels of output for the Keynesian model
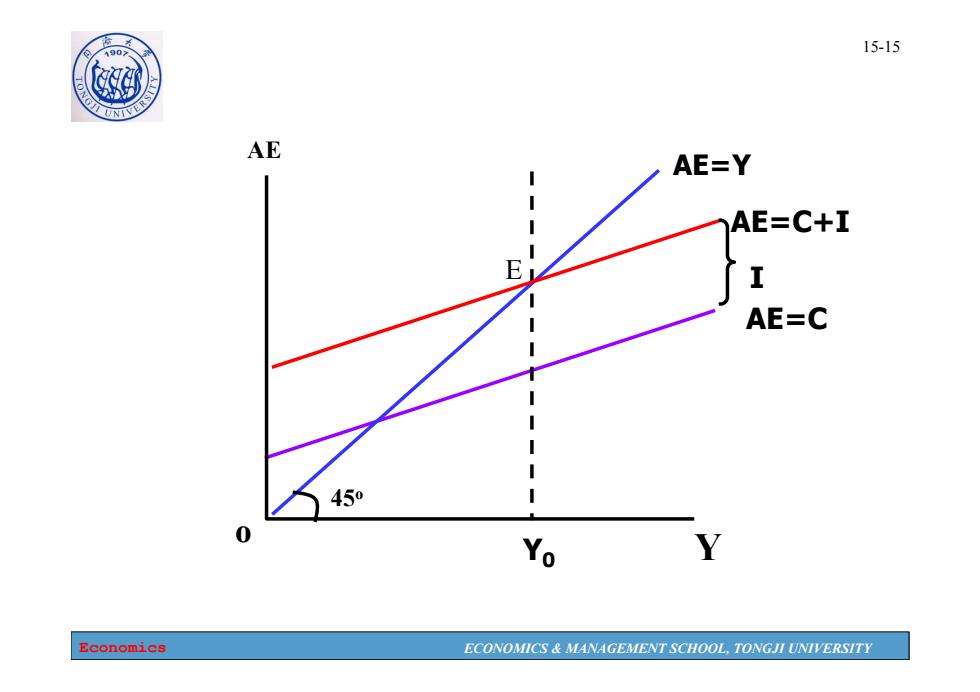
1907 15-15 AE AE=Y AE=C+I E I AE=C 1 V 450 I 0 Yo Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-15 AE=C+I Y AE o Y0 AE=C 45o I E AE=Y