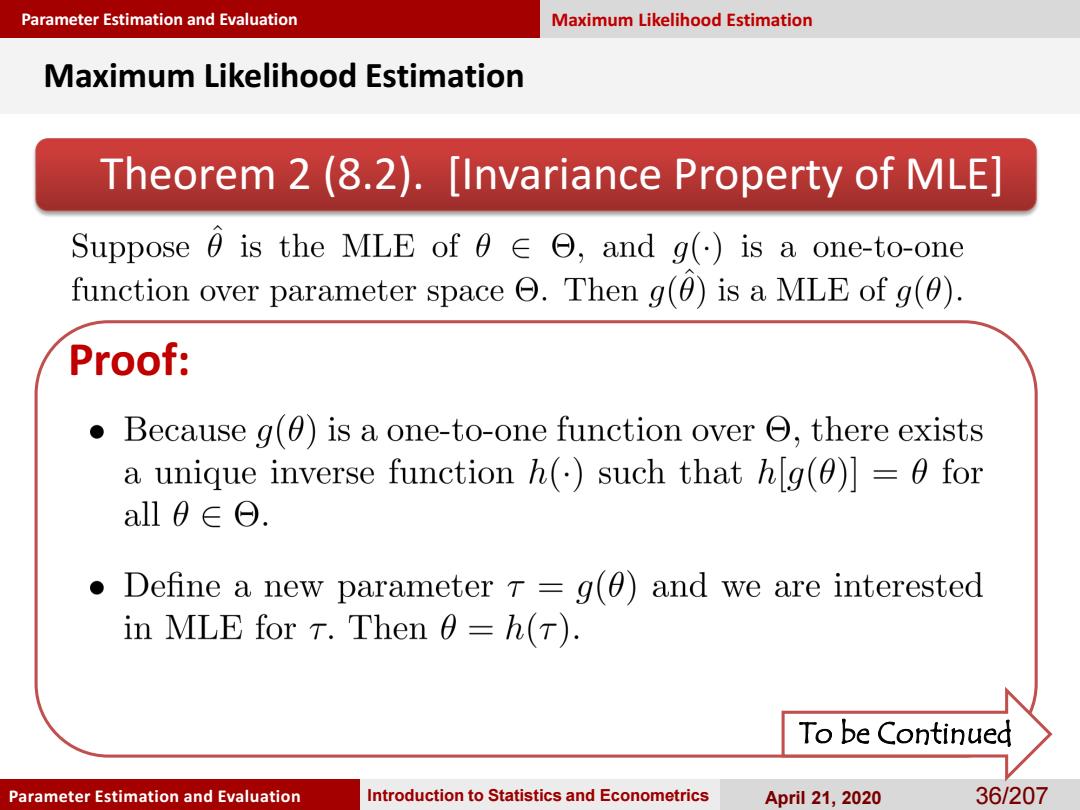
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Theorem 2(8.2).[Invariance Property of MLE] Suppose0 is the MLE of0∈Θ,andg()is a one-to-one function over parameter space Then g(0)is a MLE of g(0). Proof: 。 Because g(0)is a one-to-one function over there exists a unique inverse function h()such that h[g(0)]=0 for all0∈Θ. Define a new parameter r =g(0)and we are interested in MLE for T.Then 0=h(T). To be Continued Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21,2020 36/207
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21, 2020 36/207 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Theorem 2 (8.2). [Invariance Property of MLE] Proof: To be Continued

Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof: It follows that the likelihood function of the random sam- ple Xn i(0Xm)=[h(r)川Xm] i*(X"), where [*(X")is the likelihood function of X"with respect to the transformed parameter r. Now suppose 0 is a global MLE of 0.Then we have i(0Xm)≥i(0X")for all6∈Θ. To be Continued Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21,2020 371207
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21, 2020 37/207 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof: To be Continued
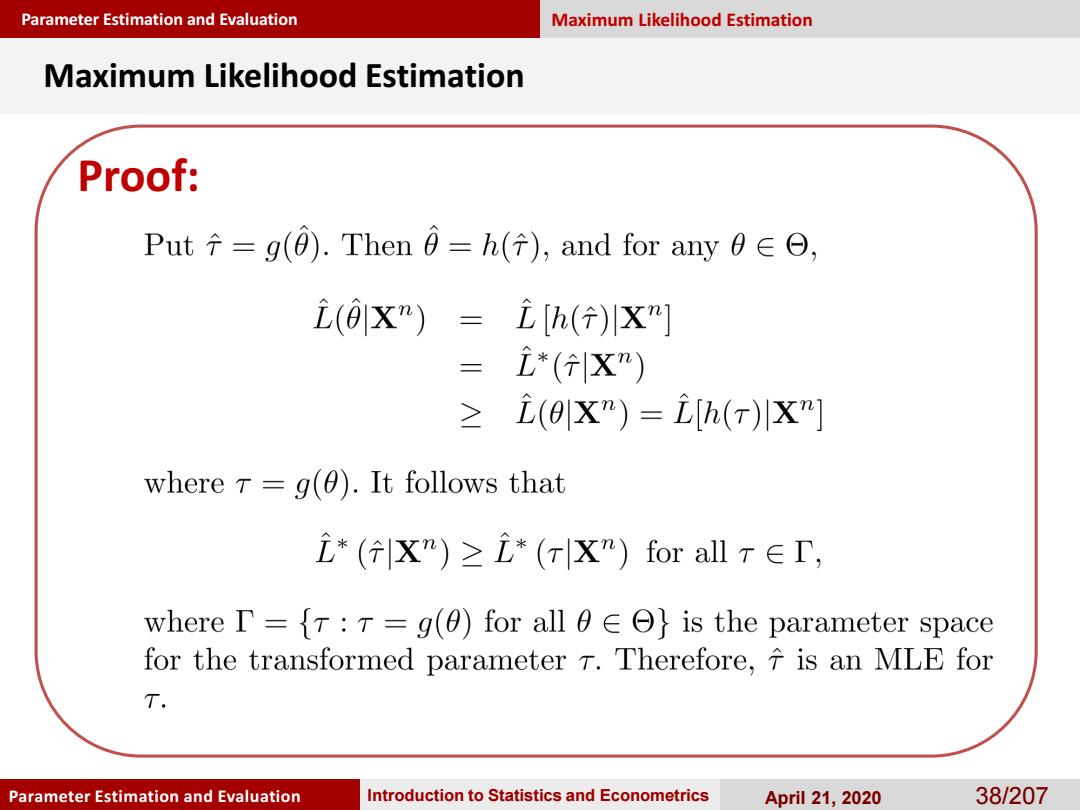
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof: Put÷=g(0).Then0=h(分),and for any0∈O, i(©X")=立[h()川X] i*(X”) ≥(0X")=[h(r)xm] where r=g(0).It follows that i*(X")≥*(rXm)for allT∈T, where I=r:T=g(0)for all 0ee}is the parameter space for the transformed parameter T.Therefore,f is an MLE for T. Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21,2020 38/207
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21, 2020 38/207 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof:
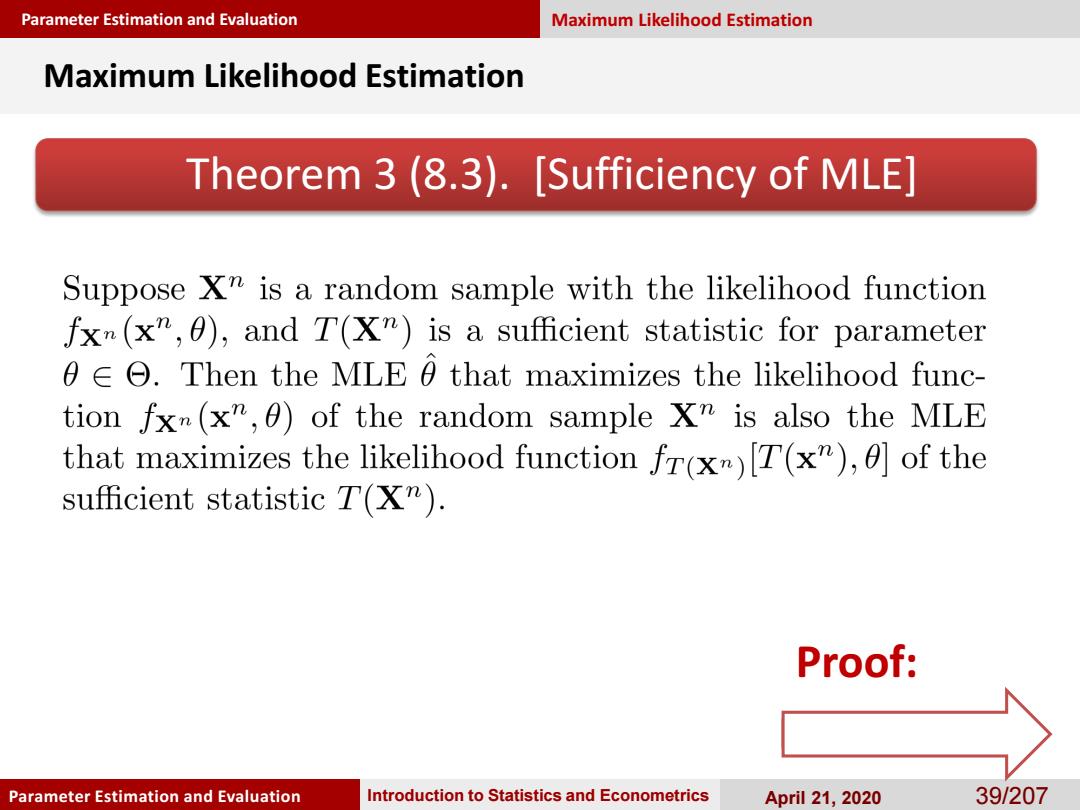
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Theorem 3(8.3).[Sufficiency of MLE] Suppose X"is a random sample with the likelihood function fxm(x",0),and T(X")is a sufficient statistic for parameter 0E O.Then the MLE 0 that maximizes the likelihood func- tion fx(x",0)of the random sample Xm is also the MLE that maximizes the likelihood function fr(x)[T(x"),0]of the sufficient statistic T(X"). Proof: Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21,2020 39/207
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21, 2020 39/207 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Theorem 3 (8.3). [Sufficiency of MLE] Proof:
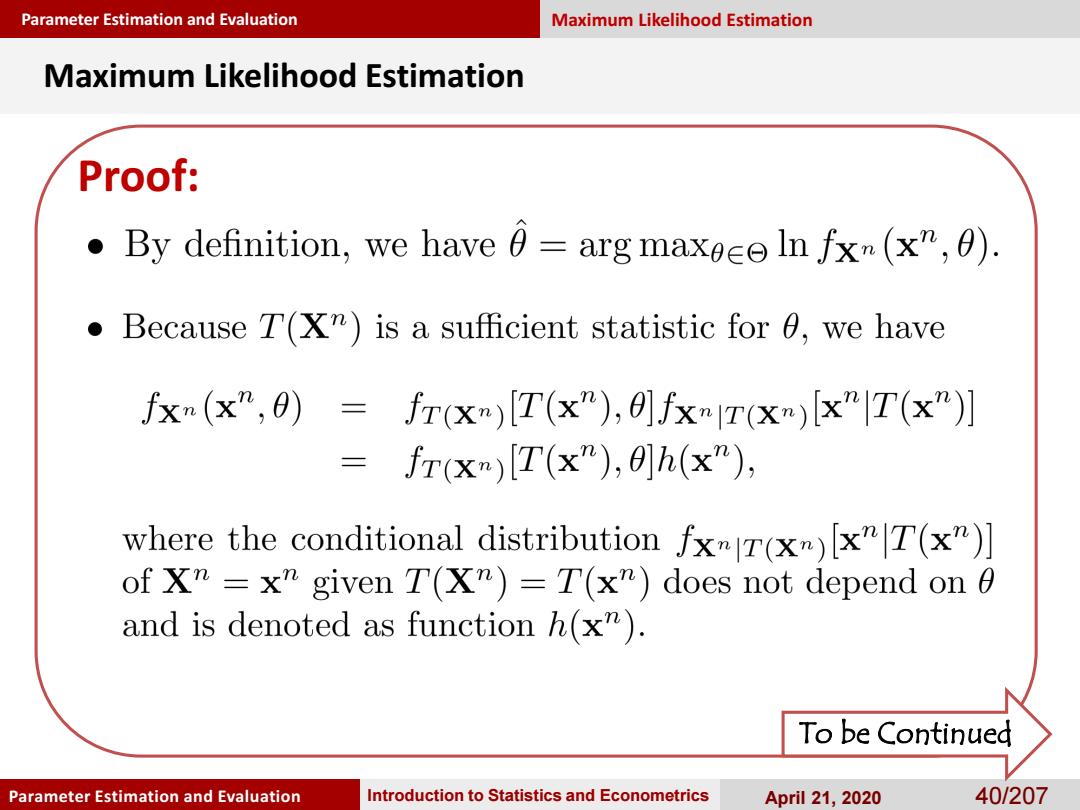
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof: By definition,we have 0=arg maxece In fxm(x",0) Because T(XR)is a sufficient statistic for 0,we have fxm(x”,0)=frx)[T(x”),0fxnT(xn)x”T(x"】 fr(x)[I(x"),0]h(x"), where the conditional distribution fxr(x)[x"T(x")] of Xm=x"given T(Xm)=T(x")does not depend on 0 and is denoted as function h(x"). To be Continued Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21,2020 40/207
Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Parameter Estimation and Evaluation Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 21, 2020 40/207 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Maximum Likelihood Estimation Proof: To be Continued